Objective Detection of Eloquent Axonal Pathways to Minimize Postoperative Deficits in Pediatric Epilepsy Surgery using Diffusion Tractography and Convolutional Neural Networks
- PMID: 30835220
- PMCID: PMC9016495
- DOI: 10.1109/TMI.2019.2902073
Objective Detection of Eloquent Axonal Pathways to Minimize Postoperative Deficits in Pediatric Epilepsy Surgery using Diffusion Tractography and Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract
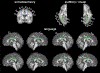
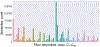
Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have recently been used in biomedical imaging applications with great success. In this paper, we investigated the classi?cation performance of CNN models on diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) streamlines de?ned by functional MRI (fMRI) and electrical stimulation mapping (ESM). To learn a set of discriminative and interpretable features from the extremely unbalanced dataset, we evaluated different CNN architectures with multiple loss functions (e.g., focal loss and center loss) and a soft attention mechanism, and compared our models with current state-ofthe-art methods. Through extensive experiments on streamlines collected from 70 healthy children and 70 children with focal epilepsy, we demonstrated that our deep CNN model with focal and central losses and soft attention outperforms all existing models in the literature and provides clinically acceptable accuracy (73 -100%) for the objective detection of functionally-important white matter pathways including ESM determined eloquent areas such as primary motor, aphasia, speech arrest, auditory, and visual functions. The ?ndings of this study encourage further investigations to determine if DWICNN analysis can serve as a noninvasive diagnostic tool during pediatric presurgical planning by estimating not only the location of essential cortices at the gyral level, but also the underlying ?bers connecting these cortical areas, to minimize or predict postsurgical functional de?cits. This study translates an advanced CNN model to clinical practice in the pediatric population where currently available approaches (e.g., ESM, fMRI) are suboptimal. The implementation will be released at https://github. com/HaotianMXu/Brain-?ber-classi?cation-using-CNNs.
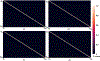
Figures



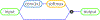
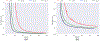





Similar articles
-
Localization of specific language pathways using diffusion-weighted imaging tractography for presurgical planning of children with intractable epilepsy.Epilepsia. 2015 Jan;56(1):49-57. doi: 10.1111/epi.12863. Epub 2014 Dec 8. Epilepsia. 2015. PMID: 25489639 Free PMC article.
-
Automatic detection of primary motor areas using diffusion MRI tractography: comparison with functional MRI and electrical stimulation mapping.Epilepsia. 2013 Aug;54(8):1381-90. doi: 10.1111/epi.12199. Epub 2013 Jun 17. Epilepsia. 2013. PMID: 23772829 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of postoperative deficits using an improved diffusion-weighted imaging maximum a posteriori probability analysis in pediatric epilepsy surgery.J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2019 Feb 22;23(5):648-659. doi: 10.3171/2018.11.PEDS18601. Print 2019 May 1. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2019. PMID: 30797207 Free PMC article.
-
Narrative review of epilepsy: getting the most out of your neuroimaging.Transl Pediatr. 2021 Apr;10(4):1078-1099. doi: 10.21037/tp-20-261. Transl Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34012857 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional MRI for Surgery of Gliomas.Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2017 Aug 23;19(10):34. doi: 10.1007/s11940-017-0469-y. Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28831723 Review.
Cited by
-
Can Deep Learning Hit a Moving Target? A Scoping Review of Its Role to Study Neurological Disorders in Children.Front Comput Neurosci. 2021 May 5;15:670489. doi: 10.3389/fncom.2021.670489. eCollection 2021. Front Comput Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34025380 Free PMC article.
-
Computational approaches for the reconstruction of optic nerve fibers along the visual pathway from medical images: a comprehensive review.Front Neurosci. 2023 May 26;17:1191999. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1191999. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37304011 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deep Learning-Based Tract Classification of Preoperative DWI Tractography Advances the Prediction of Short-Term Postoperative Language Improvement in Children With Drug-Resistant Epilepsy.IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2025 Feb;72(2):565-576. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2024.3463481. Epub 2025 Jan 21. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2025. PMID: 39292577
-
Prediction of baseline expressive and receptive language function in children with focal epilepsy using diffusion tractography-based deep learning network.Epilepsy Behav. 2021 Apr;117:107909. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2021.107909. Epub 2021 Mar 16. Epilepsy Behav. 2021. PMID: 33740493 Free PMC article.
-
Superficial white matter analysis: An efficient point-cloud-based deep learning framework with supervised contrastive learning for consistent tractography parcellation across populations and dMRI acquisitions.Med Image Anal. 2023 Apr;85:102759. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2023.102759. Epub 2023 Jan 23. Med Image Anal. 2023. PMID: 36706638 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wyllie E, “Invasive neurophysiologic techniques in the evaluation for epilepsy surgery in children,” Epilepsy surgery, pp. 409–412, 1991.
-
- Medina LS, Bernal B, Dunoyer C, Cervantes L, Rodriguez M, Pacheco E, Jayakar P, Morrison G, Ragheb J, and Altman NR, “Seizure disorders: functional mr imaging for diagnostic evaluation and surgical treatmentprospective study,” Radiology, vol. 236, no. 1, pp. 247–253, 2005. - PubMed
-
- de Ribaupierre S, Fohlen M, Bulteau C, Dorfmüller G, Delalande O, Dulac O, Chiron C, and Hertz-Pannier L, “Presurgical language mapping in children with epilepsy: clinical usefulness of functional magnetic resonance imaging for the planning of cortical stimulation,” Epilepsia, vol. 53, no. 1, pp. 67–78, 2012. - PubMed

