Novel Brain-Penetrating Oxime Acetylcholinesterase Reactivators Attenuate Organophosphate-Induced Neuropathology in the Rat Hippocampus
- PMID: 30835286
- PMCID: PMC6542341
- DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kfz060
Novel Brain-Penetrating Oxime Acetylcholinesterase Reactivators Attenuate Organophosphate-Induced Neuropathology in the Rat Hippocampus
Abstract
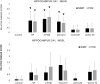
Organophosphate (OP) anticholinesterases cause excess acetylcholine leading to seizures which, if prolonged, result in neuronal damage in the rodent brain. Novel substituted phenoxyalkyl pyridinium oximes have previously shown evidence of penetrating the rat blood-brain barrier (BBB) in in vivo tests with a sarin surrogate (nitrophenyl isopropyl methylphosphonate, NIMP) or the active metabolite of the insecticide parathion, paraoxon (PXN), by reducing the time to cessation of seizure-like behaviors and accumulation of glial fibrillary acidic protein, whereas 2-PAM did not. The neuroprotective ability of our lead oximes (15, 20, and 55) was tested using NeuN, Nissl, and Fluoro-Jade B staining in the rat hippocampus. Following lethal-level subcutaneous challenge with NIMP or PXN, rats were intramuscularly administered a novel oxime or 2-PAM plus atropine and euthanized at 4 days. There were statistically significant increases in the median damage scores of the NeuN-stained NIMP, NIMP/2-PAM, and NIMP/Oxime 15 groups compared with the control whereas the scores of the NIMP/Oxime 20 and NIMP/Oxime 55 were not significantly different from the control. The same pattern of statistical significance was observed with PXN. Nissl staining provided a similar pattern, but without statistical differences. Fluoro-Jade B indicated neuroprotection from PXN with novel oximes but not with 2-PAM. The longer blood residence times of Oximes 20 and 55 compared with Oxime 15 might have contributed to their greater efficacy. These results suggest that novel oximes 20 and 55 were able to penetrate the BBB and attenuate neuronal damage after NIMP and PXN exposure, indicating potential broad-spectrum usefulness.
Keywords: acetylcholinesterase inhibitors; neuropathology; neuroprotection; organophosphate; oxime reactivators.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society of Toxicology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
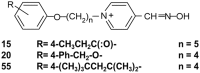


References
-
- Anderson K. J., Miller K. M., Fugaccia I., Scheff S. W. (2005). Regional distribution of Fluoro-Jade B staining in the hippocampus following traumatic brain injury. Exp. Neurol. 193, 125–130. - PubMed
-
- Baille V., Clarke P., Brochier G., Dorandeu F., Verna J., Four E., Lallement G., Carpentier P. (2005). Soman-induced convulsions: The neuropathology revisited. Toxicology 215, 1–24. - PubMed
-
- Benjamini Y., Hochberg Y. (1995). Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. Roy. Stat. Soc. B 57, 289–300.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

