Energy metabolism couples hepatocyte integrin-linked kinase to liver glucoregulation and postabsorptive responses of mice in an age-dependent manner
- PMID: 30835508
- PMCID: PMC6732653
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00496.2018
Energy metabolism couples hepatocyte integrin-linked kinase to liver glucoregulation and postabsorptive responses of mice in an age-dependent manner
Abstract
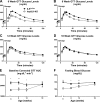
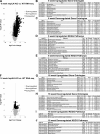
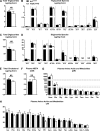
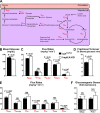
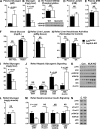
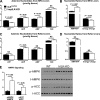
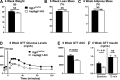
Integrin-linked kinase (ILK) is a critical intracellular signaling node for integrin receptors. Its role in liver development is complex, as ILK deletion at E10.5 (before hepatocyte differentiation) results in biochemical and morphological differences that resolve as mice age. Nevertheless, mice with ILK depleted specifically in hepatocytes are protected from the hepatic insulin resistance during obesity. Despite the potential importance of hepatocyte ILK to metabolic health, it is unknown how ILK controls hepatic metabolism or glucoregulation. The present study tested the role of ILK in hepatic metabolism and glucoregulation by deleting it specifically in hepatocytes, using a cre-lox system that begins expression at E15.5 (after initiation of hepatocyte differentiation). These mice develop the most severe morphological and glucoregulatory abnormalities at 6 wk, but these gradually resolve with age. After identifying when the deletion of ILK caused a severe metabolic phenotype, in depth studies were performed at this time point to define the metabolic programs that coordinate control of glucoregulation that are regulated by ILK. We show that 6-wk-old ILK-deficient mice have higher glucose tolerance and decreased net glycogen synthesis. Additionally, ILK was shown to be necessary for transcription of mitochondrial-related genes, oxidative metabolism, and maintenance of cellular energy status. Thus, ILK is required for maintaining hepatic transcriptional and metabolic programs that sustain oxidative metabolism, which are required for hepatic maintenance of glucose homeostasis.
Keywords: glucose homeostasis; glycogen metabolism; hepatocyte signaling; in vivo physiology; integrin signaling; liver metabolism.
Figures





References
-
- Afgan E, Baker D, Batut B, van den Beek M, Bouvier D, Cech M, Chilton J, Clements D, Coraor N, Grüning BA, Guerler A, Hillman-Jackson J, Hiltemann S, Jalili V, Rasche H, Soranzo N, Goecks J, Taylor J, Nekrutenko A, Blankenberg D. The Galaxy platform for accessible, reproducible and collaborative biomedical analyses: 2018 update. Nucleic Acids Res 46: W537–W544, 2018. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky379. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

