The Benefits and Burdens of Pediatric Palliative Care and End-of-Life Research: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 30835596
- PMCID: PMC6755658
- DOI: 10.1089/jpm.2018.0483
The Benefits and Burdens of Pediatric Palliative Care and End-of-Life Research: A Systematic Review
Abstract
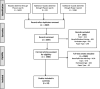
Objective: The aim of this study is to report the benefits and burdens of palliative research participation on children, siblings, parents, clinicians, and researchers. Background: Pediatric palliative care requires research to mature the science and improve interventions. A tension exists between the desire to enhance palliative and end-of-life care for children and their families and the need to protect these potentially vulnerable populations from untoward burdens. Methods: Systematic review followed PRISMA guidelines with prepared protocol registered as PROSPERO #CRD42018087304. MEDLINE, CINAHL, PsycINFO, EMBASE, Scopus, and The Cochrane Library were searched (2000-2017). English-language studies depicting the benefits or burdens of palliative care or end-of-life research participation on either pediatric patients and/or their family members, clinicians, or study teams were eligible for inclusion. Study quality was appraised using the Mixed Methods Appraisal Tool (MMAT). Results: Twenty-four studies met final inclusion criteria. The benefit or burden of palliative care research participation was reported for the child in 6 papers; siblings in 2; parents in 19; clinicians in 3; and researchers in 5 papers. Benefits were more heavily emphasized by patients and family members, whereas burdens were more prominently emphasized by researchers and clinicians. No paper utilized a validated benefit/burden scale. Discussion: The lack of published exploration into the benefits and burdens of those asked to take part in pediatric palliative care research and those conducting the research is striking. There is a need for implementation of a validated benefit/burden instrument or interview measure as part of pediatric palliative and end-of-life research design and reporting.
Keywords: benefits and burdens; palliative care research; pediatric palliative care.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing financial interests exist.
Human subjects were not involved in this systematic review methodology.
Figures

References
-
- Twycross RG: Research and palliative care: The pursuit of reliable knowledge. Palliat Med 1993;7:175–177 - PubMed
-
- Burnell RH, O'Keefe M: Asking parents unaskable questions. Lancet 2004;364:737–738 - PubMed
-
- Lantos JD: Should institutional review board decisions be evidence-based? Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 2007;161:516–517 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

