Ghrelin Upregulates Oncogenic Aurora A to Promote Renal Cell Carcinoma Invasion
- PMID: 30836712
- PMCID: PMC6468656
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers11030303
Ghrelin Upregulates Oncogenic Aurora A to Promote Renal Cell Carcinoma Invasion
Abstract
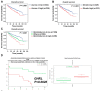
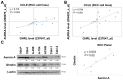
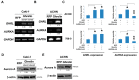
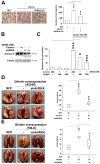
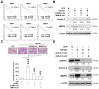
Ghrelin is a peptide hormone, originally identified from the stomach, that functions as an endogenous ligand of the growth hormone secretagogue receptor (GHSR) and promotes growth hormone (GH) release and food intake. Increasing reports point out ghrelin's role in cancer progression. We previously characterized ghrelin's prognostic significance in the clear cell subtype of renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC), and its pro-metastatic ability via Snail-dependent cell migration. However, ghrelin's activity in promoting cell invasion remains obscure. In this study, an Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA)-based investigation of differentially expressed genes in Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia (CCLE) dataset indicated the potential association of Aurora A with ghrelin in ccRCC metastasis. In addition, a significant correlation between ghrelin and Aurora A expression level in 15 ccRCC cell line was confirmed by variant probes. ccRCC patients with high ghrelin and Aurora A status were clinically associated with poor outcome. We further observed that ghrelin upregulated Aurora A at the protein and RNA levels and that ghrelin-induced ccRCC in vitro invasion and in vivo metastasis occurred in an Aurora A-dependent manner. Furthermore, MMP1, 2, 9 and 10 expressions are associated with poor outcome. In particular, MMP10 is significantly upregulated and required for the ghrelin-Aurora A axis to promote ccRCC invasion. The results of this study indicated a novel signaling mechanism in ccRCC metastasis.
Keywords: MMP10; aurora A; ghrelin; invasion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

