A Deep Convolutional Neural Network Inspired by Auditory Perception for Underwater Acoustic Target Recognition
- PMID: 30836716
- PMCID: PMC6427555
- DOI: 10.3390/s19051104
A Deep Convolutional Neural Network Inspired by Auditory Perception for Underwater Acoustic Target Recognition
Abstract
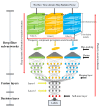
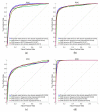
Underwater acoustic target recognition (UATR) using ship-radiated noise faces big challenges due to the complex marine environment. In this paper, inspired by neural mechanisms of auditory perception, a new end-to-end deep neural network named auditory perception inspired Deep Convolutional Neural Network (ADCNN) is proposed for UATR. In the ADCNN model, inspired by the frequency component perception neural mechanism, a bank of multi-scale deep convolution filters are designed to decompose raw time domain signal into signals with different frequency components. Inspired by the plasticity neural mechanism, the parameters of the deep convolution filters are initialized randomly, and the is n learned and optimized for UATR. The n, max-pooling layers and fully connected layers extract features from each decomposed signal. Finally, in fusion layers, features from each decomposed signal are merged and deep feature representations are extracted to classify underwater acoustic targets. The ADCNN model simulates the deep acoustic information processing structure of the auditory system. Experimental results show that the proposed model can decompose, model and classify ship-radiated noise signals efficiently. It achieves a classification accuracy of 81.96%, which is the highest in the contrast experiments. The experimental results show that auditory perception inspired deep learning method has encouraging potential to improve the classification performance of UATR.
Keywords: auditory perception inspired; brain-inspired; deep learning; filter learning; ship-radiated noise; underwater acoustic target recognition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Auditory Inspired Convolutional Neural Networks for Ship Type Classification with Raw Hydrophone Data.Entropy (Basel). 2018 Dec 19;20(12):990. doi: 10.3390/e20120990. Entropy (Basel). 2018. PMID: 33266713 Free PMC article.
-
Ship Type Classification by Convolutional Neural Networks with Auditory-like Mechanisms.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Jan 1;20(1):253. doi: 10.3390/s20010253. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 31906314 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Underwater Acoustic Target Recognition Method Based on MFCC and RACNN.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Jan 2;24(1):273. doi: 10.3390/s24010273. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38203134 Free PMC article.
-
A Survey of Underwater Acoustic Data Classification Methods Using Deep Learning for Shoreline Surveillance.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Mar 11;22(6):2181. doi: 10.3390/s22062181. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35336352 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review of Brain-Inspired Cognition and Navigation Technology for Mobile Robots.Cyborg Bionic Syst. 2024 Jun 27;5:0128. doi: 10.34133/cbsystems.0128. eCollection 2024. Cyborg Bionic Syst. 2024. PMID: 38938902 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Passive Detection of Ship-Radiated Acoustic Signal Using Coherent Integration of Cross-Power Spectrum with Doppler and Time Delay Compensations.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Mar 22;20(6):1767. doi: 10.3390/s20061767. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32235803 Free PMC article.
-
Underwater Target Signal Classification Using the Hybrid Routing Neural Network.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Nov 24;21(23):7799. doi: 10.3390/s21237799. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34883803 Free PMC article.
-
Underwater acoustic target recognition method based on a joint neural network.PLoS One. 2022 Apr 29;17(4):e0266425. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0266425. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35486577 Free PMC article.
-
Underwater Acoustic Target Recognition Based on Attention Residual Network.Entropy (Basel). 2022 Nov 15;24(11):1657. doi: 10.3390/e24111657. Entropy (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36421512 Free PMC article.
-
Recognition of Underwater Materials of Bionic and Natural Fishes Based on Blue-Green Light Reflection.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Dec 7;22(24):9600. doi: 10.3390/s22249600. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36559971 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Meng Q., Yang S. A wave structure based method for recognition of marine acoustic target signals. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2015;137:2242. doi: 10.1121/1.4920186. - DOI
-
- Das A., Kumar A., Bahl R. Marine vessel classification based on passive sonar data: The cepstrum-based approach. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2013;7:87–93. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2011.0142. - DOI
-
- Wei X., Li G., Wang Z.Q. Underwater target recognition based on wavelet packet and principal component analysis. Comput. Simul. 2011;28:8–290. doi: 10.1090/S0002-9939-2011-10775-5. - DOI
-
- Yang H., Shen S. The Feature Selection of Pattern Recognition. Publishing House of Electronic Industry; Beijing, China: 2016.
-
- Yang H., Gan A., Chen H., Yue P., Tang J., Li J. Underwater acoustic target recognition using SVM ensemble via weighted sample and feature selection; Proceedings of the 13th International Bhurban Conference on Applied Sciences and Technology; Islamabad, Pakistan. 12–16 January 2016; - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

