Post-Traumatic Stress, Quality of Life and Alcohol Use Problems among Out-of-School Youth
- PMID: 30836738
- PMCID: PMC6444102
- DOI: 10.30773/pi.2018.12.25.3
Post-Traumatic Stress, Quality of Life and Alcohol Use Problems among Out-of-School Youth
Abstract
Objective: Post-traumatic stress symptoms (PTSS) in out-of-school youths (OSYs) may be influenced by alcohol use, but there is a lack of evidence explaining how PTSS affect alcohol use problems in OSYs. The present study aimed to investigate the relationships among PTSS, quality of life, and alcohol use in OSYs.
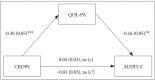
Methods: In total, 125 OSYs (46.4% male) in South Korea completed the Korean Version of the Child Report of Post-Traumatic Symptoms (CROPS), the KIDSCREEN-27 Quality of Life Measure for Children and Adolescents, and the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test-Consumption.
Results: Mean CROPS score was 18.7 (SD=11.6); 37.6% were problem drinkers. Quality of life in the domain of parent relations and autonomy significantly mediated the relationship between PTSS and alcohol use problems. OSYs with high parental satisfaction and autonomy were less likely to have alcohol use problems even with PTSS.
Conclusion: Family assessments and therapeutic approaches are needed for OSYs with both PTSS and alcohol use problems.
Keywords: Adolescent; Alcohol drinking; Post-traumatic stress disorder; Quality of life; Student dropout.
Figures
References
-
- Ministry of Gender Equality and Family Youth white paper. Korea: Sejong; 2016. Available at: http://www.mogef.go.kr/mp/pcd/mp_pcd_s001d.do;jsessionid=AzKR+Gfe83eQrxo.... Accessed August 9, 2018.
-
- Gyeonggido Family and Women Research Institute What is the solution to the problem of stopping youth study? Available at: https://www.gfwri.kr/2012/issue/no44/issue44.pdf. Suwon: Korea; 2012. Accessed August 9, 2018.
-
- Dyregrov A. Educational consequences of loss and trauma. Educ Child Psychol. 2004;21:77–84.
-
- Schnurr PP, Friedman MJ, Bernardy NC. Research on posttraumatic stress disorder: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and assessment. J Clin Psychol. 2002;58:877–889. - PubMed
-
- Doey T. Treating trauma and traumatic grief in children and adolescents. J Can Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2010;19:54–55.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

