Large air-filled intrapulmonary bronchogenic cyst associated with tension pneumothorax during air travel
- PMID: 30837238
- PMCID: PMC6424296
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2018-228032
Large air-filled intrapulmonary bronchogenic cyst associated with tension pneumothorax during air travel
Abstract
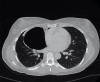
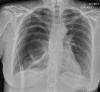
A 38-year-old woman developed a spontaneous right-sided tension pneumothorax during light aircraft travel. The aircraft was diverted to a regional centre, where emergent needle thoracostomy and chest tube insertion were performed. History suggested that this was the second episode of pneumothorax, with an untreated event with similar symptomatology during air travel 1 year ago. She was taken for surgical intervention. Intraoperative findings were of a large right middle lobe cyst of uncertain origin; the procedure was subsequently aborted. A CT chest demonstrated a large multiseptated air-filled pulmonary cystic lesion. Inpatient stay was notable for persistent right pneumothorax with interval cyst rupture. A right middle lobectomy was subsequently performed with histopathology showing a benign epithelioid bronchogenic cyst. Recovery was unremarkable with no residual pneumothorax or further episodes at 2 months postoperatively. Preventative excision of air-filled pulmonary abnormalities should be considered prior to air travel.
Keywords: air leaks; cardiothoracic surgery; pneumothorax; respiratory medicine.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2019. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures









References
-
- Parkin L, Bell ML, Herbison GP, et al. . Air travel and fatal pulmonary embolism. Thromb Haemost 2006;95:807–14. - PubMed
-
- Beunderman R, Sramek M, Koster RW, et al. . [Criteria for differential diagnosis in cardial symptoms; left- or right-sided chest pain?]. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd 1990;134:2249–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
