Sleep increases chromosome dynamics to enable reduction of accumulating DNA damage in single neurons
- PMID: 30837464
- PMCID: PMC6401120
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-08806-w
Sleep increases chromosome dynamics to enable reduction of accumulating DNA damage in single neurons
Abstract
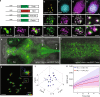
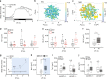
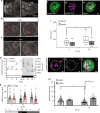
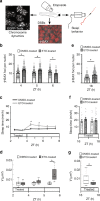
Sleep is essential to all animals with a nervous system. Nevertheless, the core cellular function of sleep is unknown, and there is no conserved molecular marker to define sleep across phylogeny. Time-lapse imaging of chromosomal markers in single cells of live zebrafish revealed that sleep increases chromosome dynamics in individual neurons but not in two other cell types. Manipulation of sleep, chromosome dynamics, neuronal activity, and DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) showed that chromosome dynamics are low and the number of DSBs accumulates during wakefulness. In turn, sleep increases chromosome dynamics, which are necessary to reduce the amount of DSBs. These results establish chromosome dynamics as a potential marker to define single sleeping cells, and propose that the restorative function of sleep is nuclear maintenance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Comment in
-
Sleep: DNA Repair Function for Better Neuronal Aging?Curr Biol. 2019 Jun 17;29(12):R585-R588. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2019.05.018. Curr Biol. 2019. PMID: 31211981
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

