Inhibition of avian-origin influenza A(H7N9) virus by the novel cap-dependent endonuclease inhibitor baloxavir marboxil
- PMID: 30837531
- PMCID: PMC6401108
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-39683-4
Inhibition of avian-origin influenza A(H7N9) virus by the novel cap-dependent endonuclease inhibitor baloxavir marboxil
Abstract
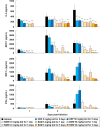
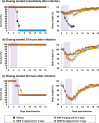
Human infections with avian-origin influenza A(H7N9) virus represent a serious threat to global health; however, treatment options are limited. Here, we show the inhibitory effects of baloxavir acid (BXA) and its prodrug baloxavir marboxil (BXM), a first-in-class cap-dependent endonuclease inhibitor, against A(H7N9), in vitro and in vivo. In cell culture, BXA at four nanomolar concentration achieved a 1.5-2.8 log reduction in virus titers of A(H7N9), including the NA-R292K mutant virus and highly pathogenic avian influenza viruses, whereas NA inhibitors or favipiravir required approximately 20-fold or higher concentrations to achieve the same levels of reduction. A(H7N9)-specific amino acid polymorphism at position 37, implicated in BXA binding to the PA endonuclease domain, did not impact on BXA susceptibility. In mice, oral administration of BXM at 5 and 50 mg/kg twice a day for 5 days completely protected from a lethal A/Anhui/1/2013 (H7N9) challenge, and reduced virus titers more than 2-3 log in the lungs. Furthermore, the potent therapeutic effects of BXM in mice were still observed when a higher virus dose was administered or treatment was delayed up to 48 hours post infection. These findings support further investigation of BXM for A(H7N9) treatment in humans.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors K.T., Y.A., H.N., S.T., T.N., M. Kawai., R.Y., A.S., T.S. and A.N. are employees of Shionogi & Co., Ltd. The authors K.M., M.O., Y.S. and H.K. were provided financial support from Shionogi & Co., Ltd. for the studies performed in the manuscript. The author M. Kobayashi. was an employee of Shionogi & Co., Ltd., and now declares no potential conflict of interest. All works reported here were financially supported by Shionogi & Co., Ltd..
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

