Primary sclerosing cholangitis and inflammatory bowel disease comorbidity: an update of the evidence
- PMID: 30837784
- PMCID: PMC6394256
- DOI: 10.20524/aog.2019.0344
Primary sclerosing cholangitis and inflammatory bowel disease comorbidity: an update of the evidence
Abstract
Comorbid primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) represent a unique disease phenotype with a different risk profile than PSC or IBD alone. While the pathogenetic mechanisms behind both diseases remain unclear, recent studies have targeted several immune-mediated pathways in an attempt to find a potential therapeutic target. Patients with PSC-associated IBD typically exhibit pancolitis with a right-to-left intestinal inflammatory gradient associated with a greater incidence of backwash ileitis and rectal sparing. Although there is an increased incidence of pancolitis in this population, bowel symptoms tend to be less significant than in IBD alone. Likewise, the degree of inflammation and symptoms of PSC-associated IBD are characteristically less clinically significant. Despite the relatively quiescent clinical presentation of PSC-associated IBD, there is an increased risk for colorectal and hepatobiliary malignancy making vigilance for malignancy essential.
Keywords: Crohn’s disease; Primary sclerosing cholangitis; inflammatory bowel disease; ulcerative colitis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: None
Figures
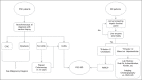
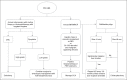
References
-
- Rasmussen HH, Fallingborg JF, Mortensen PB, Vyberg M, Tage-Jensen U, Rasmussen SN. Hepatobiliary dysfunction and primary sclerosing cholangitis in patients with Crohn's disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1997;32:604–610. - PubMed
-
- Takikawa H, Takamori Y, Tanaka A, Kurihara H, Nakanuma Y. Analysis of 388 cases of primary sclerosing cholangitis in Japan;presence of a subgroup without pancreatic involvement in older patients. Hepatol Res. 2004;29:153–159. - PubMed
-
- Ang TL, Fock KM, Ng TM, Teo EK, Chua TS, Tan JY. Clinical profile of primary sclerosing cholangitis in Singapore. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002;17:908–913. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
