Hydrogen Sulfide Oxidation: Adaptive Changes in Mitochondria of SW480 Colorectal Cancer Cells upon Exposure to Hypoxia
- PMID: 30838088
- PMCID: PMC6374825
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/8102936
Hydrogen Sulfide Oxidation: Adaptive Changes in Mitochondria of SW480 Colorectal Cancer Cells upon Exposure to Hypoxia
Abstract
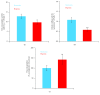
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S), a known inhibitor of cytochrome c oxidase (CcOX), plays a key signaling role in human (patho)physiology. H2S is synthesized endogenously and mainly metabolized by a mitochondrial sulfide-oxidizing pathway including sulfide:quinone oxidoreductase (SQR), whereby H2S-derived electrons are injected into the respiratory chain stimulating O2 consumption and ATP synthesis. Under hypoxic conditions, H2S has higher stability and is synthesized at higher levels with protective effects for the cell. Herein, working on SW480 colon cancer cells, we evaluated the effect of hypoxia on the ability of cells to metabolize H2S. The sulfide-oxidizing activity was assessed by high-resolution respirometry, measuring the stimulatory effect of sulfide on rotenone-inhibited cell respiration in the absence or presence of antimycin A. Compared to cells grown under normoxic conditions (air O2), cells exposed for 24 h to hypoxia (1% O2) displayed a 1.3-fold reduction in maximal sulfide-oxidizing activity and 2.7-fold lower basal O2 respiration. Based on citrate synthase activity assays, mitochondria of hypoxia-treated cells were 1.8-fold less abundant and displayed 1.4-fold higher maximal sulfide-oxidizing activity and 2.6-fold enrichment in SQR as evaluated by immunoblotting. We speculate that under hypoxic conditions mitochondria undergo these adaptive changes to protect cell respiration from H2S poisoning.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Hydrogen sulfide perturbs mitochondrial bioenergetics and triggers metabolic reprogramming in colon cells.J Biol Chem. 2019 Aug 9;294(32):12077-12090. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.009442. Epub 2019 Jun 18. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31213529 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidation of H2S in mammalian cells and mitochondria.Methods Enzymol. 2015;554:201-28. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2014.11.042. Epub 2015 Jan 22. Methods Enzymol. 2015. PMID: 25725524
-
Oxidation of hydrogen sulfide remains a priority in mammalian cells and causes reverse electron transfer in colonocytes.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Aug;1797(8):1500-11. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2010.04.004. Epub 2010 Apr 14. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 20398623
-
Essential role of sulfide oxidation in brain health and neurological disorders.Pharmacol Ther. 2025 Feb;266:108787. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2024.108787. Epub 2024 Dec 22. Pharmacol Ther. 2025. PMID: 39719173 Review.
-
Hydrogen sulfide as an oxygen sensor.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2013 Mar 1;51(3):623-32. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2012-0551. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2013. PMID: 23196804 Review.
Cited by
-
The Hidden Role of Hydrogen Sulfide Metabolism in Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 18;22(12):6562. doi: 10.3390/ijms22126562. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34207284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hydrogen Sulfide Biology and Its Role in Cancer.Molecules. 2022 May 25;27(11):3389. doi: 10.3390/molecules27113389. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35684331 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sequential Accumulation of 'Driver' Pathway Mutations Induces the Upregulation of Hydrogen-Sulfide-Producing Enzymes in Human Colonic Epithelial Cell Organoids.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Sep 15;11(9):1823. doi: 10.3390/antiox11091823. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36139896 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogen Sulfide: Emerging Role in Bladder, Kidney, and Prostate Malignancies.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Nov 3;2019:2360945. doi: 10.1155/2019/2360945. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 31781328 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging pharmacological tools to control hydrogen sulfide signaling in critical illness.Intensive Care Med Exp. 2020 Jan 31;8(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s40635-020-0296-4. Intensive Care Med Exp. 2020. PMID: 32006269 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cooper C. E., Brown G. C. The inhibition of mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase by the gases carbon monoxide, nitric oxide, hydrogen cyanide and hydrogen sulfide: chemical mechanism and physiological significance. Journal of Bioenergetics and Biomembranes. 2008;40(5):533–539. doi: 10.1007/s10863-008-9166-6. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

