Nucleolar protein nucleolin functions in replication stress-induced DNA damage responses
- PMID: 30839063
- PMCID: PMC6530621
- DOI: 10.1093/jrr/rry114
Nucleolar protein nucleolin functions in replication stress-induced DNA damage responses
Abstract
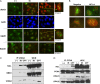
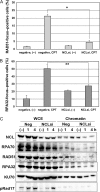
The nucleolus contains multiple copies of ribosomal (r)DNA, which indicate sites of frequent replication stress and suggest the existence of a mechanism to prevent replication stress-related rDNA instability and the possibility that such a mechanism contributes to the whole genomic stability against replication stress. We have previously reported that nucleolin, a major nucleolar protein, is involved in ionizing radiation-induced DNA damage responses (DDRs) such as ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM)-dependent cell cycle checkpoints and homologous recombination (HR) repair. Here, we investigated the role of nucleolin in DDR due to replication stress. The results indicate that following replication stress, nucleolin interacted with the histone γH2AX, proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), and replication protein A (RPA)32, suggesting that it may be recruited to DNA damage sites on the replication fork. Furthermore, the knockdown of nucleolin by siRNA reduced the activation of ATM and RAD3-related (ATR) kinase and the formation of RAD51 and RPA32 foci after replication stress due to UV or camptothecin exposure, whereas nucleolin overexpression augmented ATR-dependent phosphorylation and RAD51 and RPA accumulation on chromatin. Moreover, these overexpressing cells seemed to increase repair activity and resistance to replication stress. Our results indicate that nucleolin plays an important role in replication stress-induced DDRs such as ATR activation and HR repair. Given that nucleolin overexpression is often observed in many types of cancer cells, our findings suggest that nucleolin is involved in the regulation of resistance to replication stress that may otherwise lead to tumorigenesis and it could be a possible target for chemotherapy and radiotherapy.
Keywords: ATR; DNA damage; nucleolin; nucleolus; replication stress.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Japan Radiation Research Society and Japanese Society for Radiation Oncology.
Figures


References
-
- Saito Y, Zhou H, Kobayashi J. Chromatin modification and NBS1: their relationship in DNA double-strand break repair. Genes Genet Syst 2016;90:195–208. - PubMed
-
- Paull TT. Mechanisms of ATM Activation. Annu Rev Biochem 2015;84:711–38. - PubMed
-
- Shibata A. Regulation of repair pathway choice at two-ended DNA double-strand breaks. Mutat Res 2017;803–805:51–5. - PubMed
-
- Blackford AN, Jackson SP. ATM, ATR, and DNA-PK: the trinity at the heart of the DNA damage response. Mol Cell 2017;66:801–17. - PubMed
-
- Irony-Tur Sinai M, Kerem B. DNA replication stress drives fragile site instability. Mutat Res 2018;808:56–61. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

