Evolution of control with learning classifier systems
- PMID: 30839802
- PMCID: PMC6214302
- DOI: 10.1007/s41109-018-0088-x
Evolution of control with learning classifier systems
Abstract
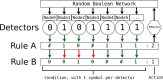
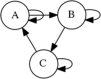
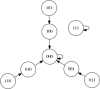
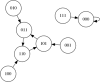
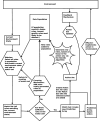
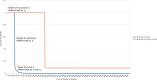
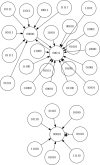
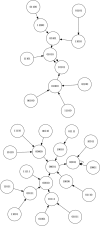
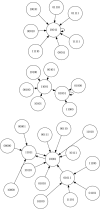
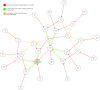
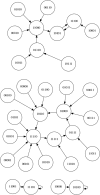
In this paper we describe the application of a learning classifier system (LCS) variant known as the eXtended classifier system (XCS) to evolve a set of 'control rules' for a number of Boolean network instances. We show that (1) it is possible to take the system to an attractor, from any given state, by applying a set of 'control rules' consisting of ternary conditions strings (i.e. each condition component in the rule has three possible states; 0, 1 or #) with associated bit-flip actions, and (2) that it is possible to discover such rules using an evolutionary approach via the application of a learning classifier system. The proposed approach builds on learning (reinforcement learning) and discovery (a genetic algorithm) and therefore the series of interventions for controlling the network are determined but are not fixed. System control rules evolve in such a way that they mirror both the structure and dynamics of the system, without having 'direct' access to either.
Keywords: Boolean network; Complex systems; Controllability; Discovery; Intervention; LCS; Learning; XCS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A study of structural and parametric learning in XCS.Evol Comput. 2006 Spring;14(1):1-19. doi: 10.1162/evco.2006.14.1.1. Evol Comput. 2006. PMID: 16536886
-
Extending XCS with Cyclic Graphs for Scalability on Complex Boolean Problems.Evol Comput. 2017 Summer;25(2):173-204. doi: 10.1162/EVCO_a_00167. Epub 2015 Sep 25. Evol Comput. 2017. PMID: 26406166
-
Accuracy-based learning classifier systems: models, analysis and applications to classification tasks.Evol Comput. 2003 Fall;11(3):209-38. doi: 10.1162/106365603322365289. Evol Comput. 2003. PMID: 14558911
-
XCSc: a novel approach to clustering with extended classifier system.Int J Neural Syst. 2011 Feb;21(1):79-93. doi: 10.1142/S0129065711002675. Int J Neural Syst. 2011. PMID: 21243732
-
Rule fitness and pathology in learning classifier systems.Evol Comput. 2004 Spring;12(1):99-135. doi: 10.1162/evco.2004.12.1.99. Evol Comput. 2004. PMID: 15096307
References
-
- Aldana, M (2003) Boolean dynamics of networks with scale-free topology. Physica D: Nonlinear Phenom 185(1):45–66. 10.1016/S0167-2789(03)00174-X. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S016727890300174X.
-
- Aldana M, Coppersmith S, Kadanoff LP. Perspectives and Problems in Nolinear Science. Amsterdam: Springer; 2003. Boolean dynamics with random couplings; pp. 23–89.
-
- Anderson PW, Arrow K, Pines D. The economy as an evolving complex system. Boulder, Colorado: Westview Press; 1988.
-
- Barry AM. The stability of long action chains in XCS. Soft Comput. 2002;6(3-4):183–199. doi: 10.1007/s005000100115. - DOI
-
- Bull, L (2009) On dynamical genetic programming: simple Boolean networks in learning classifier systems. Int J Parallel, Emergent Distrib Syst 24(5):421–442. 10.1080/17445760802660387.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
