Adult female syphilis prevalence, congenital syphilis case incidence and adverse birth outcomes, Mongolia 2000-2016: Estimates using the Spectrum STI tool
- PMID: 30839908
- PMCID: PMC6326223
- DOI: 10.1016/j.idm.2018.03.003
Adult female syphilis prevalence, congenital syphilis case incidence and adverse birth outcomes, Mongolia 2000-2016: Estimates using the Spectrum STI tool
Abstract
Introduction: Mongolia's health ministry prioritizes control of Sexually Transmitted Infections, including syphilis screening and treatment in antenatal care (ANC).
Methods: Adult syphilis prevalence trends were fitted using the Spectrum-STI estimation tool, using data from ANC surveys and routine screening over 1997-2016. Estimates were combined with programmatic data to estimate numbers of treated and untreated pregnant women with syphilis and associated incidence congenital syphilis (CS) and CS-attributable adverse birth outcomes (ABO), which we compared with CS case reports.
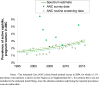
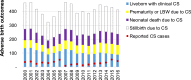
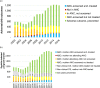
Results: Syphilis prevalence in pregnant women was estimated at 1.7% in 2000 and 3.0% in 2016. We estimated 652 CS cases, of which 410 ABO, in 2016. Far larger, annually increasing numbers of CS cases and ABO were estimated to have been prevented: 1654 cases, of which 789 ABO in 2016 - thanks to increasing coverages of ANC (99% in 2016), ANC-based screening (97% in 2016) and treatment of women diagnosed (81% in 2016). The 42 CS cases reported nationally over 2016 (liveborn infants only) represented 27% of liveborn infants with clinical CS, but only 7% of estimated CS cases among women found syphilis-infected in ANC, and 6% of all estimated CS cases including those born to women with undiagnosed syphilis.
Discussion/conclusion: Mongolia's ANC-based syphilis screening program is reducing CS, but maternal prevalence remains high. To eliminate CS (target: <50 cases per 100,000 live births), Mongolia should strengthen ANC services, limiting losses during referral for treatment, and under-diagnosis of CS including still-births and neonatal deaths, and expand syphilis screening and prevention programs.
Keywords: ABO, Adverse Birth Outcome; ANC, antenatal care; ANC-1, attendance of antenatal care at least once during a pregnancy; Antenatal care; CI, confidence interval; CS, Congenital Syphilis; Congenital syphilis; Epidemiological modelling; F, women; N, sample size tested; NCCD, Mongolia National Center for Communicable Diseases; RPR, Rapid Plasma Reagin test; STI, sexually transmitted infection; Screening; Surveillance; Syphilis; TP, Treponema pallidum; WHO, World Health Organization.
Figures
References
-
- Avenir Health . 2017. Spectrum health program planning tools, freely downloadable software. Glastonbury (Connecticut)http://spectrumbeta.futuresinstitute.org/http://avenirhealth.org/software-spectrum.php Available from:
-
- Azyei I., Aumakhan B., Jantsansengee B., Munkhbaatar S., Gombo E., Puntsag U. Evolving understanding of the epidemiology of HIV and prevention needs among men who have sex with men in Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia. AIDS and Behavior. 2014 Oct;18(10):2009–2019. - PubMed
-
- Badrakh J., Zayasaikhan S., Davaalkham J., Erdenetungalag E., Jadambaa N., Munkhbaatar S. Trends in adult chlamydia and gonorrhea prevalence, incidence and urethral discharge case reporting in Mongolia over 1995-2016 – estimates using the Spectrum-STI model. Western Pac Surveill Response J. 2017 Nov;8(4) - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

