Dynamic model of tuberculosis considering multi-drug resistance and their applications
- PMID: 30839915
- PMCID: PMC6326219
- DOI: 10.1016/j.idm.2018.11.001
Dynamic model of tuberculosis considering multi-drug resistance and their applications
Abstract
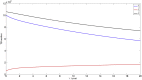
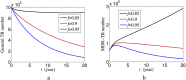
Infectious diseases have always been a problem that threatens people's health and tuberculosis is one of the major. With the development of medical scientific research, drug-resistant infectious diseases have become a more intractable threat because various drugs and antibiotics are widely used in the process of fighting against infectious diseases. In this paper, an improved dynamic model of infectious diseases considering population dynamics and drug resistance is established. The feasible region, equilibrium points and stability of the model are analyzed. Based on the existing data, this model can predict the development of the epidemic situation through numerical simulation, and put forward some relevant measures and suggestions.
Keywords: Drug-resistant tuberculosis (TB); Dynamic model of infectious disease; Numerical simulation; Stability of the equilibrium points.
Figures
References
-
- Agusto F.B., Cook J., Shelton P.D. 2015. Mathematical model of MDR-TB and XDR-TB with isolation and lost to follow-up. Abstract and applied analysis; pp. 1–21.
-
- Blower S.M., Small P.M. Control strategies for tuberculosis epidemics: New models for old problems. Science. 1996;273(5274):497–500. - PubMed
-
- Brogger S. Systems analysis in tuberculosis control: A model. American Review of Respiratory Disease. 1967;95(3):419–434. - PubMed
-
- Carvalho A.R.M., Pinto C.M. A non-integer order analysis of the impact of diabetes and resistant strains in a model for TB infection. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation. 2018;61:104–126.
-
- Castillo-Chavez C., Feng Z. To treat or not to treat: The case of tuberculosis. Journal of Mathematical Biology. 1997;35(6):629–656. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources