Reduction of Inflammation and Enhancement of Motility after Pancreatic Islet Derived Stem Cell Transplantation Following Spinal Cord Injury
- PMID: 30840970
- PMCID: PMC6411578
- DOI: 10.3340/jkns.2018.0035
Reduction of Inflammation and Enhancement of Motility after Pancreatic Islet Derived Stem Cell Transplantation Following Spinal Cord Injury
Abstract
Objective: Spinal cord injury (SCI) is a very serious health problem, usually caused by a trauma and accompanied by elevated levels of inflammation indicators. Stem cell-based therapy is promising some valuable strategies for its functional recovery. Nestinpositive progenitor and/or stem cells (SC) isolated from pancreatic islets (PI) show mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) characteristics. For this reason, we aimed to analyze the effects of rat pancreatic islet derived stem cell (rPI-SC) delivery on functional recovery, as well as the levels of inflammation factors following SCI.
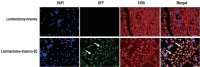
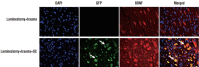
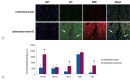
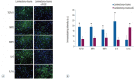
Methods: rPI-SCs were isolated, cultured and their MSC characteristics were determined through flow cytometry and immunofluorescence analysis. The experimental rat population was divided into three groups : 1) laminectomy & trauma, 2) laminectomy & trauma & phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), and 3) laminectomy+trauma+SCs. Green fluorescent protein (GFP) labelled rPI-SCs were transplanted into the injured rat spinal cord. Their motilities were evaluated with Basso, Beattie and Bresnahan (BBB) Score. After 4-weeks, spinal cord sections were analyzed for GFP labeled SCs and stained for vimentin, S100β, brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), 2',3'-cyclic-nucleotide 3'-phosphodiesterase (CNPase), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and proinflammatory (interleukin [IL]-6, transforming growth factor [TGF]-β, macrophage inflammatory protein [MIP]-2, myeloperoxidase [MPO]) and anti-inflammatory (IL-1 receptor antagonis) factors.
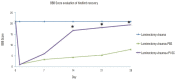
Results: rPI-SCs were revealed to display MSC characteristics and express neural and glial cell markers including BDNF, glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), fibronectin, microtubule associated protein-2a,b (MAP2a,b), β3-tubulin and nestin as well as antiinflammatory prostaglandin E2 receptor, EP3. The BBB scores showed significant motor recovery in group 3. GFP-labelled cells were localized on the injury site. In addition, decreased proinflammatory factor levels and increased intensity of anti-inflammatory factors were determined.
Conclusion: Transplantation of PI-SCs might be an effective strategy to improve functional recovery following spinal cord trauma.
Keywords: Islets of langerhans; Regeneration; Spinal cord; Stem cells; Wounds and injuries.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Post-spinal cord injury astrocyte-mediated functional recovery in rats after intraspinal injection of the recombinant adenoviral vectors Ad5-VEGF and Ad5-ANG.J Neurosurg Spine. 2017 Jul;27(1):105-115. doi: 10.3171/2016.9.SPINE15959. Epub 2017 Apr 28. J Neurosurg Spine. 2017. PMID: 28452633
-
Motor Recovery after Transplantation of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Rat Models of Spinal Cord Injury.Ann Neurosci. 2019 Jan;25(3):126-140. doi: 10.1159/000487069. Epub 2018 Apr 25. Ann Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30814821 Free PMC article.
-
[EFFECTS OF BONE MARROW MESENCHYMAL STEM CELLS TRANSPLANTATION FOR TREATING RAT SPINAL CORD INJURY AND CYTOKINE EXPRESSION AT INJURY SITES].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2016 Mar;30(3):265-71. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 27281869 Chinese.
-
Schwann cell transplantation for spinal cord injury repair: its significant therapeutic potential and prospectus.Rev Neurosci. 2015;26(2):121-8. doi: 10.1515/revneuro-2014-0068. Rev Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25581750 Review.
-
Repair of the Injured Spinal Cord by Schwann Cell Transplantation.Front Neurosci. 2022 Feb 17;16:800513. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.800513. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35250447 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mannitol Augments the Effects of Systemical Stem Cell Transplantation without Increasing Cell Migration in a Stroke Animal Model.Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2020 Oct;17(5):695-704. doi: 10.1007/s13770-020-00293-1. Epub 2020 Sep 8. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2020. PMID: 32901436 Free PMC article.
-
Cutting-edge biotechnological advancement in islet delivery using pancreatic and cellular approaches.Future Sci OA. 2020 Nov 23;7(3):FSO660. doi: 10.2144/fsoa-2020-0105. Future Sci OA. 2020. PMID: 33552541 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abdullahi D, Annuar AA, Mohamad M, Aziz I, Sanusi J. Experimental spinal cord trauma: a review of mechanically induced spinal cord injury in rat models. Rev Neurosci. 2017;28:15–20. - PubMed
-
- Aggarwal S, Pittenger MF. Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate allogeneic immune cell responses. Blood. 2005;105:1815–1822. - PubMed
-
- Ahuja CS, Nori S, Tetreault L, Wilson J, Kwon B, Harrop J, et al. Traumatic spinal cord injury-repair and regeneration. Neurosurgery. 2017;80(3S):S9–S22. - PubMed
-
- Aras Y, Sabanci PA, Kabatas S, Duruksu G, Subasi C, Erguven M, et al. The effects of adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation during the acute and subacute phases following spinal cord injury. Turk Neurosurg. 2016;26:127–139. - PubMed
-
- Basso DM, Beattie MS, Bresnahan JC. A sensitive and reliable locomotor rating scale for open field testing in rats. J Neurotrauma. 1995;12:1–21. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

