The use of acellular dermal matrix in breast reconstruction: evolution of techniques over 2 decades
- PMID: 30842922
- PMCID: PMC6378261
- DOI: 10.21037/gs.2018.10.05
The use of acellular dermal matrix in breast reconstruction: evolution of techniques over 2 decades
Abstract
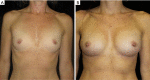
Acellular dermal matrices (ADMs) are biotechnologically derived tissues that have become a cornerstone of implant-based breast reconstruction over the last 2 decades. Their use in both dual-plane and prepectoral approaches have provided greater soft tissue coverage and implant support with good cosmetic outcomes and low rates of complication. This review describes the evolution of notable ADM-assisted surgical techniques that have advanced the field and broadened implant-based reconstructive options.
Keywords: Acellular dermal matrix (ADM); breast cancer; breast reconstruction.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Terino EO. Alloderm acellular dermal graft: applications in aesthetic soft-tissue augmentation. Clin Plast Surg 2001;28:83-99. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
