Genotype-structure-phenotype relationships diverge in paralogs ATP1A1, ATP1A2, and ATP1A3
- PMID: 30842972
- PMCID: PMC6384024
- DOI: 10.1212/NXG.0000000000000303
Genotype-structure-phenotype relationships diverge in paralogs ATP1A1, ATP1A2, and ATP1A3
Abstract
Objective: We tested the assumption that closely related genes should have similar pathogenic variants by analyzing >200 pathogenic variants in a gene family with high neurologic impact and high sequence identity, the Na,K-ATPases ATP1A1, ATP1A2, and ATP1A3.
Methods: Data sets of disease-associated variants were compared. Their equivalent positions in protein crystal structures were used for insights into pathogenicity and correlated with the phenotype and conservation of homology.
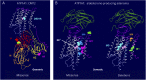
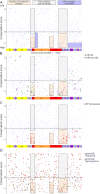
Results: Relatively few mutations affected the corresponding amino acids in 2 genes. In the membrane domain of ATP1A3 (primarily expressed in neurons), variants producing milder neurologic phenotypes had different structural positions than variants producing severe phenotypes. In ATP1A2 (primarily expressed in astrocytes), membrane domain variants characteristic of severe phenotypes in ATP1A3 were absent from patient data. The known variants in ATP1A1 fell into 2 distinct groups. Sequence conservation was an imperfect indicator: it varied among structural domains, and some variants with demonstrated pathogenicity were in low conservation sites.
Conclusions: Pathogenic variants varied between genes despite high sequence identity, and there is a genotype-structure-phenotype relationship in ATP1A3 that correlates with neurologic outcomes. The absence of "severe" pathogenic variants in ATP1A2 patients predicts that they will manifest either in a different tissue or by death in utero and that new ATP1A1 variants will produce additional phenotypes. It is important that some variants in poorly conserved amino acids are nonetheless pathogenic and could be incorrectly predicted to be benign.
Figures




References
-
- Azizan EA, Brown MJ. Novel genetic determinants of adrenal aldosterone regulation. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 2016;23:209–217. - PubMed
-
- Barcroft LC, Moseley AE, Lingrel JB, Watson AJ. Deletion of the Na/K-ATPase α1-subunit gene (Atp1a1) does not prevent cavitation of the preimplantation mouse embryo. Mech Dev 2004;121:417–426. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
