Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and nuclear factor-κB play important roles in regulating programmed cell death ligand 1 expression by epidermal growth factor receptor mutants in non-small-cell lung cancer cells
- PMID: 30844110
- PMCID: PMC6500984
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.13989
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and nuclear factor-κB play important roles in regulating programmed cell death ligand 1 expression by epidermal growth factor receptor mutants in non-small-cell lung cancer cells
Abstract
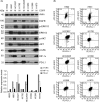
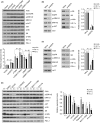
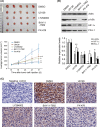
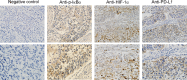
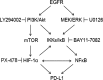
Some driver gene mutations, including epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), have been reported to be involved in expression regulation of the immunosuppressive checkpoint protein programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1), but the underlying mechanism remains obscure. We investigated the potential role and precise mechanism of EGFR mutants in PD-L1 expression regulation in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells. Examination of pivotal EGFR signaling effectors in 8 NSCLC cell lines indicated apparent associations between PD-L1 overexpression and phosphorylation of AKT and ERK, especially with increased protein levels of phospho-IκBα (p-IκBα) and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α). Flow cytometry results showed stronger membrane co-expression of EGFR and PD-L1 in NSCLC cells with EGFR mutants compared with cells carrying WT EGFR. Additionally, ectopic expression or depletion of EGFR mutants and treatment with EGFR pathway inhibitors targeting MEK/ERK, PI3K/AKT, mTOR/S6, IκBα, and HIF-1α indicated strong accordance among protein levels of PD-L1, p-IκBα, and HIF-1α in NSCLC cells. Further treatment with pathway inhibitors significantly inhibited xenograft tumor growth and p-IκBα, HIF-1α, and PD-L1 expression of NSCLC cells carrying EGFR mutant in nude mice. Moreover, immunohistochemical analysis revealed obviously increased protein levels of p-IκBα, HIF-1α, and PD-L1 in NSCLC tissues with EGFR mutants compared with tissues carrying WT EGFR. Non-small-cell lung cancer tissues with either p-IκBα or HIF-1α positive staining were more likely to possess elevated PD-L1 expression compared with tissues scored negative for both p-IκBα and HIF-1α. Our findings showed important roles of phosphorylation activation of AKT and ERK and potential interplay and cooperation between NF-κB and HIF-1α in PD-L1 expression regulation by EGFR mutants in NSCLC.
Keywords: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; NF-κB; epidermal growth factor receptor; non-small-cell lung cancer; programmed cell death ligand 1.
© 2019 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
High co-expression of PD-L1 and HIF-1α correlates with tumour necrosis in pulmonary pleomorphic carcinoma.Eur J Cancer. 2016 Jun;60:125-35. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2016.03.012. Epub 2016 Apr 22. Eur J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27107327
-
ILT4 inhibition prevents TAM- and dysfunctional T cell-mediated immunosuppression and enhances the efficacy of anti-PD-L1 therapy in NSCLC with EGFR activation.Theranostics. 2021 Jan 19;11(7):3392-3416. doi: 10.7150/thno.52435. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33537094 Free PMC article.
-
Mutational activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor down-regulates major histocompatibility complex class I expression via the extracellular signal-regulated kinase in non-small cell lung cancer.Cancer Sci. 2019 Jan;110(1):52-60. doi: 10.1111/cas.13860. Epub 2018 Nov 27. Cancer Sci. 2019. PMID: 30390416 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Pathway, Yes-Associated Protein (YAP) and the Regulation of Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1) in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC).Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Aug 5;20(15):3821. doi: 10.3390/ijms20153821. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31387256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Advances of the Role of Lung Cancer Driver Gene and PD-1/PD-L1 Pathway Interaction in the Tumorigenesis and Progression of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2017 Nov 20;20(11):781-786. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2017.11.10. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 29167009 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Plasmatic Levels of HSP90α at Diagnosis: A Novel Prognostic Indicator of Clinical Outcome in Advanced Lung Cancer Patients Treated With PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitors Plus Chemotherapy.Front Oncol. 2021 Dec 3;11:765115. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.765115. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34926266 Free PMC article.
-
Immunotherapy against programmed death-1/programmed death ligand 1 in hepatocellular carcinoma: Importance of molecular variations, cellular heterogeneity, and cancer stem cells.World J Stem Cells. 2021 Jul 26;13(7):795-824. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i7.795. World J Stem Cells. 2021. PMID: 34367478 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NF-κB and Its Role in Checkpoint Control.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 31;21(11):3949. doi: 10.3390/ijms21113949. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32486375 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Advances in the Influence of EGFR Mutation on the PD-L1 Expression in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2019 Dec 20;22(12):779-785. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2019.12.08. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31874674 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
CircCDR1as upregulates autophagy under hypoxia to promote tumor cell survival via AKT/ERK½/mTOR signaling pathways in oral squamous cell carcinomas.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Oct 3;10(10):745. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1971-9. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 31582727 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel R, De Santis C, Virgo K, et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;62:220‐241. - PubMed
-
- Kocher F, Hilbe W, Seeber A, et al. Longitudinal analysis of 2293 NSCLC patients: a comprehensive study from the TYROL registry. Lung Cancer. 2015;87:193‐200. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 7152029/Beijing Municipal Natural Science Foundation
- 7172045/Beijing Municipal Natural Science Foundation
- 2016YFC0902300/National Key Research and Development Project Precision Medicine Special Research
- 81101778/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81472206/National Natural Science Foundation of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

