A Quarter Century of APOE and Alzheimer's Disease: Progress to Date and the Path Forward
- PMID: 30844401
- PMCID: PMC6407643
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2019.01.056
A Quarter Century of APOE and Alzheimer's Disease: Progress to Date and the Path Forward
Abstract
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is considered a polygenic disorder. This view is clouded, however, by lingering uncertainty over how to treat the quasi "monogenic" role of apolipoprotein E (APOE). The APOE4 allele is not only the strongest genetic risk factor for AD, it also affects risk for cardiovascular disease, stroke, and other neurodegenerative disorders. This review, based mostly on data from human studies, ranges across a variety of APOE-related pathologies, touching on evolutionary genetics and risk mitigation by ethnicity and sex. The authors also address one of the most fundamental question pertaining to APOE4 and AD: does APOE4 increase AD risk via a loss or gain of function? The answer will be of the utmost importance in guiding future research in AD.
Keywords: AD; APOE; ASO; Alzheimer’s disease; Apolipoprotein E; anti-sense oligonucleotide; cardiovascular disease; ethnicity; evolutionary genetics; gene-based therapy; neurodegenerative disease; pleiotropy; sex.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
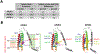
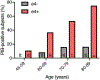

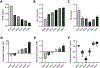
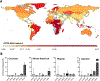
References
-
- Adams D, Gonzalez-Duarte A, O’Riordan WD, Yang C-C, Ueda M, Kristen AV, Tournev I, Schmidt HH, Coelho T, Berk JL, et al. (2018). Patisiran, an RNAi Therapeutic, for Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis. N. Engl. J. Med 379, 11–21. - PubMed
-
- Agosta F, Vossel KA, Miller BL, Migliaccio R, Bonasera SJ, Filippi M, Boxer AL, Karydas A, Possin KL, and Gorno-Tempini ML (2009). Apolipoprotein E ε4 is associated with disease-specific effects on brain atrophy in Alzheimer’s disease and frontotemporal dementia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci 106, 2018–2022. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

