Overweight and Obesity in the Russian Population: Prevalence in Adults and Association with Socioeconomic Parameters and Cardiovascular Risk Factors
- PMID: 30844809
- PMCID: PMC6465691
- DOI: 10.1159/000493885
Overweight and Obesity in the Russian Population: Prevalence in Adults and Association with Socioeconomic Parameters and Cardiovascular Risk Factors
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the prevalence and geographic distribution of overweight and obesity in Russian adults aged 25-64 years as well as the association between chronic risk factors and obesity.
Methods: Data were obtained from the survey "Epidemiology of Cardiovascular Diseases and Its Risk Factors in Some Regions of the Russian Federation" (ESSE-RF). This is a large cross-sectional multicenter population-based study that included interviews and medical examination (anthropometry, blood pressure [BP] measurement, and laboratory analysis) applied in 2012-2014.
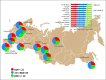
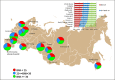
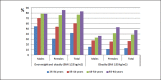
Results: The sample included 20,190 adults (response rate 79.4%) aged 25-64 years. Approximately one third of participants (30.3%) had obesity and another third (34.3%) were classified as overweight. BMI increased with age in both sexes. The prevalence of obesity between regions ranged from 24.4 to 35.5%. Overweight and obesity levels decreased with higher education (men only). Overall obesity rates were higher in rural than urban populations, but rates of overweight were similar in rural and urban populations. Participants with obesity were more likely to have BP > 160/100 mm Hg (odds ratio > 2.0) and also > 140/90 mm Hg, raised blood glucose, and high triglycerides.
Conclusion: The prevalence of overweight and obesity in Russian adults aged 25-64 years is not evenly distributed geographically, but it is comparable to that of other European countries. Individuals with obesity were also more likely to have indicators of poor cardiovascular and metabolic health.
Keywords: Epidemiology; Obesity; Overweight; Prevalence; Risk factors; Russian Federation; Socioeconomic factors.
© 2019 The Author(s) Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures
References
-
- Huffman SK, Rizov M. The rise of obesity in transition: theory and empirical evidence from russia. J Dev Stud. 2010;46((3)):574–94.
-
- Martinchik AN, Baturin AK, Keshabyants EE, Peskova EV. [Gender and age characteristics and the trends in prevalence of obesity in the adult population in Russia during the 1994-2012 period] Vopr Pitan. 2015;84((3)):50–7. - PubMed
-
- Scientific Organizing Committee of the ESSE-RF Epidemiology of cardiovascular diseases in different regions of russia (ESSE-RF). the rationale for and design of the study. Prev Med. 2013;6:25.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical