EMT Regulation by Autophagy: A New Perspective in Glioblastoma Biology
- PMID: 30845654
- PMCID: PMC6468412
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers11030312
EMT Regulation by Autophagy: A New Perspective in Glioblastoma Biology
Abstract
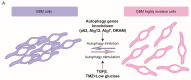
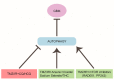
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and its reverse process MET naturally occur during development and in tissue repair in vertebrates. EMT is also recognized as the crucial event by which cancer cells acquire an invasive phenotype through the activation of specific transcription factors and signalling pathways. Even though glial cells have a mesenchymal phenotype, an EMT-like process tends to exacerbate it during gliomagenesis and progression to more aggressive stages of the disease. Autophagy is an evolutionary conserved degradative process that cells use in order to maintain a proper homeostasis, and defects in autophagy have been associated to several pathologies including cancer. Besides modulating cell resistance or sensitivity to therapy, autophagy also affects the migration and invasion capabilities of tumor cells. Despite this evidence, few papers are present in literature about the involvement of autophagy in EMT-like processes in glioblastoma (GBM) so far. This review summarizes the current understanding of the interplay between autophagy and EMT in cancer, with special regard to GBM model. As the invasive behaviour is a hallmark of GBM aggressiveness, defining a new link between autophagy and EMT can open a novel scenario for targeting these processes in future therapeutical approaches.
Keywords: Wnt/β-catenin signalling; autophagy; cadherins; epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT); glioblastoma (GBM).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

