RhoTermPredict: an algorithm for predicting Rho-dependent transcription terminators based on Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis and Salmonella enterica databases
- PMID: 30845912
- PMCID: PMC6407284
- DOI: 10.1186/s12859-019-2704-x
RhoTermPredict: an algorithm for predicting Rho-dependent transcription terminators based on Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis and Salmonella enterica databases
Abstract
Background: In bacterial genomes, there are two mechanisms to terminate the DNA transcription: the "intrinsic" or Rho-independent termination and the Rho-dependent termination. Intrinsic terminators are characterized by a RNA hairpin followed by a run of 6-8 U residues relatively easy to identify using one of the numerous available prediction programs. In contrast, Rho-dependent termination is mediated by the Rho protein factor that, firstly, binds to ribosome-free mRNA in a site characterized by a C > G content and then reaches the RNA polymerase to induce its release. Conversely on intrinsic terminators, the computational prediction of Rho-dependent terminators in prokaryotes is a very difficult problem because the sequence features required for the function of Rho are complex and poorly defined. This is the reason why it still does not exist an exhaustive Rho-dependent terminators prediction program.
Results: In this study we introduce RhoTermPredict, the first published algorithm for an exhaustive Rho-dependent terminators prediction in bacterial genomes. RhoTermPredict identifies these elements based on a previously proposed consensus motif common to all Rho-dependent transcription terminators. It essentially searches for a 78 nt long RUT site characterized by a C > G content and with regularly spaced C residues, followed by a putative pause site for the RNA polymerase. We tested RhoTermPredict performances by using available genomic and transcriptomic data of the microorganism Escherichia coli K-12, both in limited-length sequences and in the whole-genome, and available genomic sequences from Bacillus subtilis 168 and Salmonella enterica LT2 genomes. We also estimated the overlap between the predictions of RhoTermPredict and those obtained by the predictor of intrinsic terminators ARNold webtool. Our results demonstrated that RhoTermPredict is a very performing algorithm both for limited-length sequences (F1-score obtained about 0.7) and for a genome-wide analysis. Furthermore the degree of overlap with ARNold predictions was very low.
Conclusions: Our analysis shows that RhoTermPredict is a powerful tool for Rho-dependent terminators search in the three analyzed genomes and could fill this gap in computational genomics. We conclude that RhoTermPredict could be used in combination with an intrinsic terminators predictor in order to predict all the transcription terminators in bacterial genomes.
Keywords: Motif; RUT site; Rho; Rho-dependent terminators; RhoTermPredict; Transcription termination.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

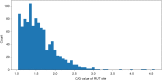
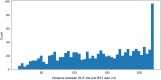
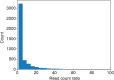
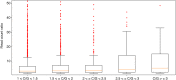
Similar articles
-
Prediction of transcriptional terminators in Bacillus subtilis and related species.PLoS Comput Biol. 2005 Aug;1(3):e25. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.0010025. Epub 2005 Aug 12. PLoS Comput Biol. 2005. PMID: 16110342 Free PMC article.
-
Parameters affecting transcription termination by Escherichia coli RNA. II. Construction and analysis of hybrid terminators.J Mol Biol. 1992 Mar 5;224(1):53-63. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90575-5. J Mol Biol. 1992. PMID: 1372366
-
Parameters affecting transcription termination by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. I. Analysis of 13 rho-independent terminators.J Mol Biol. 1992 Mar 5;224(1):31-51. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90574-4. J Mol Biol. 1992. PMID: 1372365
-
Rho-dependent terminators and transcription termination.Microbiology (Reading). 2006 Sep;152(Pt 9):2515-2528. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.28982-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2006. PMID: 16946247 Review.
-
Rho Protein: Roles and Mechanisms.Annu Rev Microbiol. 2017 Sep 8;71:687-709. doi: 10.1146/annurev-micro-030117-020432. Epub 2017 Jul 21. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28731845 Review.
Cited by
-
TSS-Captur: a user-friendly pipeline for characterizing unclassified RNA transcripts.NAR Genom Bioinform. 2024 Dec 18;6(4):lqae168. doi: 10.1093/nargab/lqae168. eCollection 2024 Dec. NAR Genom Bioinform. 2024. PMID: 39703424 Free PMC article.
-
Antisense transcription is associated with expression of metal resistance determinants in Cupriavidus metallidurans CH34.Metallomics. 2024 Dec 2;16(12):mfae057. doi: 10.1093/mtomcs/mfae057. Metallomics. 2024. PMID: 39562278 Free PMC article.
-
Premature termination of transcription is shaped by Rho and translated uORFS in Mycobacterium tuberculosis.iScience. 2023 Mar 22;26(4):106465. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106465. eCollection 2023 Apr 21. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37096044 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping the Complex Transcriptional Landscape of the Phytopathogenic Bacterium Dickeya dadantii.mBio. 2022 Jun 28;13(3):e0052422. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00524-22. Epub 2022 May 2. mBio. 2022. PMID: 35491820 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of AggR levels reveals features of virulence regulation in enteroaggregative E. coli.Commun Biol. 2021 Nov 16;4(1):1295. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-02820-9. Commun Biol. 2021. PMID: 34785760 Free PMC article.
References
-
- d’Aubenton Carafa Y, Brody E, Thermes C. Prediction of rho-independent Escherichia coli transcription terminators. A statistical analysis of their RNA stem-loop structures J Mol Biol. 1990;216:835–858. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

