Association of age and colostrum discarding with breast-feeding practice in Ethiopia: systematic review and meta-analyses
- PMID: 30846022
- PMCID: PMC10260488
- DOI: 10.1017/S1368980019000314
Association of age and colostrum discarding with breast-feeding practice in Ethiopia: systematic review and meta-analyses
Abstract
Objective: To investigate whether maternal/caregiver's age, infant age (0-6 months) and discarding colostrum affects timely initiation of breast-feeding (TIBF) and exclusive breast-feeding (EBF) in Ethiopia.
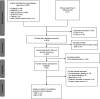
Design: A systematic search of PubMed, SCOPUS, EMBASE, CINHAL, Web of Science and WHO Global Health Library electronic databases was done for all articles published in English from 2000 to January 2018. Two reviewers independently screened, extracted and graded the quality of studies using Newcastle-Ottawa Scale. A weighted inverse-variance random-effects model meta-analysis, cumulative meta-analysis and mixed-effects meta-regression analysis were done.
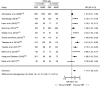
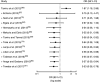
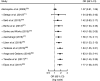
Setting: All observational studies conducted in Ethiopia.ParticipantsMothers of children aged less than 2 years.ResultA total of forty articles (fourteen studies on TIBF and twenty-six on EBF) were included. TIBF was associated with colostrum discarding (OR=0·38; 95 % CI 0·21, 0·68) but not with maternal/caregiver's age (OR=0·98; 95 % CI 0·83, 1·15). In addition, colostrum discarding (OR=0·53; 95 % CI 0·36, 0·78) and infant age (OR=1·77; 95 % CI 1·38, 2·27) were significantly associated with EBF but not maternal/caregiver's age (OR=1·09; 95 % CI 0·84, 1·41).
Conclusions: There was no association between maternal/caregiver's age and breast-feeding practice (EBF and TIBF). Colostrum discarding was associated with both EBF and TIBF. This evidence could be helpful to counsel all mothers of reproductive age and who discard colostrum.
Keywords: Breast-feeding; Ethiopia; Infant; Maternal age; Meta-analysis; Review.
Figures







References
-
- World Health Organization (2008) Indicators for Assessing Infant and Young Child Feeding Practices: Part 1: Definitions. Conclusions of a consensus meeting held 6–8 November 2007 in Washington DC, USA. Geneva: WHO.
-
- World Health Organization (2003) Global Strategy for Infant and Young Child Feeding. Geneva: WHO.
-
- World Health Organization (2003) Complementary Feeding: Report of the Global Consultation, and Summary of Guiding Principles for Complementary Feeding of the Breastfed Child. Geneva: WHO.
-
- UNICEF & World Health Organization (2017) Global Breastfeeding Scorecard, 2017: Tracking Progress for Breastfeeding Policies and Programmes. https://www.who.int/nutrition/publications/infantfeeding/global-bf-score... (accessed February 2019).

