B-Type Natriuretic Peptide During Treatment With Sacubitril/Valsartan: The PARADIGM-HF Trial
- PMID: 30846338
- PMCID: PMC7955687
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.01.018
B-Type Natriuretic Peptide During Treatment With Sacubitril/Valsartan: The PARADIGM-HF Trial
Abstract
Background: Natriuretic peptides are substrates of neprilysin; hence, B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) concentrations rise with neprilysin inhibition. Thus, the clinical validity of measuring BNP in sacubitril/valsartan-treated patients has been questioned, and use of N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptides (NT-proBNP) has been preferred and recommended.
Objectives: The purpose of this study was to determine the prognostic performance of BNP measurements before and during treatment with sacubitril/valsartan.
Methods: BNP and NT-proBNP were measured before and after 4 to 6 weeks, 8 to 10 weeks, and 9 months of treatment with sacubitril/valsartan in the PARADIGM-HF (Prospective Comparison of ARNI with ACEI to Determine Impact on Global Mortality and Morbidity in Heart Failure) trial. We assessed the association of levels of these natriuretic peptides with the subsequent risk of cardiovascular death or hospitalization for HF.
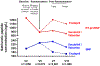
Results: Median BNP concentration (before treatment: 202 ng/l [Q1 to Q3: 126 to 335 ng/l]) increased to 235 ng/l (Q1 to Q3: 128 to 422 ng/l) after 8 to 10 weeks of treatment. BNP concentrations doubled in 141 (18%) patients and tripled in 49 (6%) patients during the first 8 to 10 weeks of sacubitril/valsartan. In contrast, such striking increases in NT-proBNP following the use of the neprilysin inhibitor were extremely rare. Treatment with sacubitril/valsartan caused a rightward shift in the distribution of BNP when compared with NT-proBNP, but both peptides retained their prognostic accuracy (C-statistics of 63% to 67% for BNP and C-statistics of 64% to 70% for NT-proBNP) with no difference between the 2 biomarkers. Increases in both BNP and NT-proBNP during 8 to 10 weeks of sacubitril/valsartan were associated with worse outcomes (p = 0.003 and p = 0.005, respectively).
Conclusions: Circulating levels of BNP may increase meaningfully early after initiation of sacubitril/valsartan. In comparison, NT-proBNP is not a substrate of neprilysin inhibition, and thus may lead to less clinical confusion when measured within 8 to 10 weeks of drug initiation. However, during treatment, either biomarker predicts the risk of major adverse outcomes in patients treated with angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitors. (Prospective Comparison of ARNI with ACEI to Determine Impact on Global Mortality and Morbidity in Heart Failure [PARADIGM-HF]; NCT01035255).
Keywords: biomarker; heart failure; natriuretic peptides; prognostication; risk stratification; treatment.
Copyright © 2019 American College of Cardiology Foundation. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
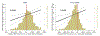

Comment in
-
What Explains the Benefits of ARNI Therapy in Heart Failure?J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019 Mar 26;73(11):1285-1287. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.01.019. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 30898203 No abstract available.
-
Searching for Optimal Prognostic Marker of Heart Failure Progression in the Era of ARNI.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019 Jul 9;74(1):164-165. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.04.044. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 31272545 No abstract available.
References
-
- Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/HFSA Focused Update of the 2013 ACCF/AHA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Failure Society of America. Circulation 2017. - PubMed
-
- Ponikowski P, Voors AA, Anker SD et al. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: The Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC)Developed with the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J 2016;37:2129–200. - PubMed
-
- Clerico A, Fontana M, Zyw L, Passino C, Emdin M. Comparison of the diagnostic accuracy of brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) and the N-terminal part of the propeptide of BNP immunoassays in chronic and acute heart failure: a systematic review. Clin Chem 2007;53:813–22. - PubMed
-
- Hammerer-Lercher A, Collinson P, van Dieijen-Visser Marja P et al. Do laboratories follow heart failure recommendations and guidelines and did we improve? The CARdiac MArker Guideline Uptake in Europe (CARMAGUE). Clin Chem Lab Med 2013:1301. - PubMed
-
- McMurray JJ, Packer M, Desai AS et al. Angiotensin-neprilysin inhibition versus enalapril in heart failure. N Engl J Med 2014;371:993–1004. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

