Emerging cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in autosomal dominant Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 30846386
- PMCID: PMC6511459
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jalz.2018.12.019
Emerging cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in autosomal dominant Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Introduction: Four less well-studied but promising "emerging" cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) biomarkers are elevated in late-onset Alzheimer disease (AD): neurogranin, synaptosomal-associated protein-25 (SNAP-25), visinin-like protein 1 (VILIP-1), and chitinase-3-like protein 1 (YKL-40).
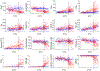
Methods: CSF neurogranin, SNAP-25, VILIP-1, and YKL-40 were measured in families carrying autosomal-dominant AD mutations.
Results: The four emerging CSF biomarkers were significantly elevated in the mutation carriers (n = 235) versus noncarriers (n = 145). CSF SNAP-25, VILIP-1, and YKL-40 were altered very early in the AD time course, approximately 15-19 years before estimated symptom onset. All CSF biomarkers predicted important AD-related outcomes including performance on a cognitive composite, brain amyloid burden as measured by amyloid positron emission tomography, and the estimated years from symptom onset.
Discussion: Early abnormalities in CSF tTau, pTau, SNAP-25, VILIP-1, and YKL-40 suggest that synaptic damage, neuronal injury, and neuroinflammation begin shortly after the commencement of brain amyloid accumulation.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Autosomal-dominant Alzheimer's disease; Biomarkers; Cerebrospinal fluid; Dementia; Neuroinflammation.
Copyright © 2019 the Alzheimer's Association. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential Conflicts of Interest
S.E.S. has a family member with stock in Eli Lilly, which is developing drugs for Alzheimer disease. D.L.G. is a full time employee at Biogen, which funded this study and is developing drugs for Alzheimer disease. L.M.S. receives research support from Eli Lilly, Hoffman LaRoche, MJFox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research for Biofind study and has served as consultant and/or advisory boards for Roche Diagnostics and Eli Lilly. He provides quality control oversight for Roche Elecsys immunoassays in the ADNI study. J.J.H. is on the advisory board and consults for both Biogen and Lundbeck A/S. T.L.S.B. consults for Eli Lilly and receives research funding from Avid Radiopharmaceuticals. J.L. reports personal fees from Aesku, Bayer Vital, the Willi Gross Foundation, Axon Neuroscience, and Ionis Pharmaceuticals. He has received non-financial support from AbbVie that is outside the submitted work. D.M.H. co-founded and is on the scientific advisory board of C2N Diagnostics. D.M.H. consults for Genentech, AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Proclara, and Denali. Washington University receives research grants to the lab of D.M.H. from C2N Diagnostics, Eli Lilly, AbbVie, and Denali. J.H.L. reports being named on patents related to the use of VILIP-1. These are being managed by Washington University in accordance with University policy. J.H.L. is a co-inventor on patent 11/630582 (2005) (Markers for brain damage) and patent 60957132 (2008) (Alzheimer’s diagnosis). J.C.M. has or is currently participating in clinical trials of anti-dementia drugs sponsored by Janssen Immunotherapy, Eli Lilly and Company, and Pfizer. He has served as a consultant for or has received speaking honoraria from Eisai, Esteve, Janssen Alzheimer Immunotherapy Program/Elan, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, and Pfizer. He receives research support from Eli Lilly/Avid Radiopharmaceuticals. R.J.B. co-founded and is on the scientific advisory board of C2N Diagnostics. He consults for Roche, Genentech, AbbVie, Pfizer, Boehringer-Ingelheim, and Merck. A.M.F. has received research funding from Biogen, Fujirebio and Roche Diagnostics. She is a member of the scientific advisory boards for Roche, Genentech and AbbVie and also consults for Araclon/Griffols and DiamiR. Y.L., K.W.T., E.M.H., R.L.H., J.D.G., G.W., J.Q.T., C.C., M.J., J.P.C., J.M.N., J.M.R., N.R.G-R., and C.X. have nothing to report.
Figures

References
-
- Price J, Ko A, Wade M, Tsou S, McKeel D, Morris J. Neuron number in the entorhinal cortex and CA1 in preclinical Alzheimer's disease. Arch Neurol. 2001;58:1395–402. - PubMed
-
- Morris J, Price J. Pathologic correlates of nondemented aging, mild cognitive impairment, and early stage Alzheimer's disease. J Mol Neurosci. 2001;17:101–18. - PubMed
-
- Sperling RA, Aisen PS, Beckett LA, Bennett DA, Craft S, Fagan AM, et al. Toward defining the preclinical stages of Alzheimer's disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer's Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer's & dementia : the journal of the Alzheimer's Association. 2011;7:280–92. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

