Single-Cell RNA Profiling of Glomerular Cells Shows Dynamic Changes in Experimental Diabetic Kidney Disease
- PMID: 30846559
- PMCID: PMC6442341
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2018090896
Single-Cell RNA Profiling of Glomerular Cells Shows Dynamic Changes in Experimental Diabetic Kidney Disease
Abstract
Background: Recent single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) analyses have offered much insight into cell-specific gene expression profiles in normal kidneys. However, in diseased kidneys, understanding of changes in specific cells, particularly glomerular cells, remains limited.
Methods: To elucidate the glomerular cell-specific gene expression changes in diabetic kidney disease, we performed scRNA-seq analysis of isolated glomerular cells from streptozotocin-induced diabetic endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS)-deficient (eNOS-/-) mice and control eNOS-/- mice.
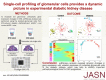
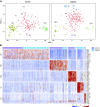
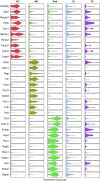
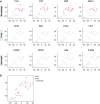
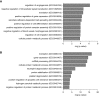
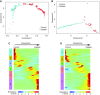
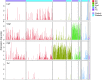
Results: We identified five distinct cell populations, including glomerular endothelial cells, mesangial cells, podocytes, immune cells, and tubular cells. Using scRNA-seq analysis, we confirmed the expression of glomerular cell-specific markers and also identified several new potential markers of glomerular cells. The number of immune cells was significantly higher in diabetic glomeruli compared with control glomeruli, and further cluster analysis showed that these immune cells were predominantly macrophages. Analysis of differential gene expression in endothelial and mesangial cells of diabetic and control mice showed dynamic changes in the pattern of expressed genes, many of which are known to be involved in diabetic kidney disease. Moreover, gene expression analysis showed variable responses of individual cells to diabetic injury.
Conclusions: Our findings demonstrate the ability of scRNA-seq analysis in isolated glomerular cells from diabetic and control mice to reveal dynamic changes in gene expression in diabetic kidneys, with variable responses of individual cells. Such changes, which might not be apparent in bulk transcriptomic analysis of glomerular cells, may help identify important pathophysiologic factors contributing to the progression of diabetic kidney disease.
Keywords: diabetic nephropathy; glomerular endothelial cells; glomerulus; macrophages; mesangial cells; transcriptional profiling.
Copyright © 2019 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures
Comment in
-
Single-cell RNA profiling of glomerular cells in diabetic kidney: a step forward for understanding diabetic nephropathy.Ann Transl Med. 2019 Dec;7(Suppl 8):S340. doi: 10.21037/atm.2019.09.104. Ann Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 32016058 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

