Climate and food diversity as drivers of mammal diversity in Inner Mongolia
- PMID: 30847099
- PMCID: PMC6392351
- DOI: 10.1002/ece3.4908
Climate and food diversity as drivers of mammal diversity in Inner Mongolia
Abstract
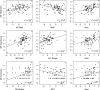
Traditionally, geographical distribution of biodiversity is assumed to be codetermined by multiple factors, for example, temperature, precipitation, environmental heterogeneity, and biotic interactions. However, few studies have simultaneously compared the relative roles of these factors in shaping the mammal diversity patterns for different feeding groups, that is, herbivores, insectivores, and carnivores. In this study, we assessed the relations between mammal diversity and current climate (mean annual temperature and precipitation), altitudinal range as well as mammal's food diversity in Inner Mongolia. Our results showed that the species richness for the three feeding guilds of mammals consistently increased with their food diversity, that is, species richness of plants, insects, and rodents. Mammal diversity also significantly decreased with mean annual temperature and precipitation. Random Forest models indicated that climate and food diversity were always included in the combinations of variables most associated with mammal diversity. Our findings suggest that while climate is an important predictor of large scale distribution of mammal diversity, biotic interactions, that is, food diversity, could also play important roles.
Keywords: biotic interactions; current climate; environmental heterogeneity; food diversity; species area relationships; species richness.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures


References
-
- Aranda, S. C. , Gabriel, R. , Borges, P. A. V. , Santos, A. M. C. , Hortal, J. , Baselga, A. , … Lobo, J. M. (2013). How do different dispersal modes shape the species‐area relationship? Evidence for between‐group coherence in the Macaronesian flora. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 22, 483–493. 10.1111/geb.12008 - DOI
-
- Araújo, M. B. , & Rozenfeld, A. (2014). The geographic scaling of biotic interactions. Ecography, 37, 406–415. 10.7287/peerj.preprints.82v1 - DOI
-
- Báldi, A. (2008). Habitat heterogeneity overrides the species‐area relationship. Journal of Biogeography, 35, 675–681. 10.1111/j.1365-2699.2007.01825.x - DOI
-
- Barrio, I. C. , Bueno, C. G. , Gartzia, M. , Soininen, E. M. , Christie, K. S. , Speed, J. D. M. , … Hik, D. S. (2016). Biotic interactions mediate patterns of herbivore diversity in the Arctic. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 25, 1108–1118. 10.1111/geb.12470 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

