Adjunctive hyperbaric oxygen therapy for irradiated rat calvarial defects
- PMID: 30847252
- PMCID: PMC6399085
- DOI: 10.5051/jpis.2019.49.1.2
Adjunctive hyperbaric oxygen therapy for irradiated rat calvarial defects
Abstract
Purpose: The aim of this study was to conduct a histologic evaluation of irradiated calvarial defects in rats 4 weeks after applying fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF-2) with hyaluronan or biphasic calcium phosphate (BCP) block in the presence or absence of adjunctive hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) therapy.
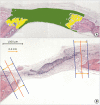
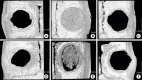
Methods: Twenty rats were divided into HBO and non-HBO (NHBO) groups, each of which was divided into FGF-2 and BCP-block subgroups according to the grafted material. Localized radiation with a single 12-Gy dose was applied to the calvaria of rats to simulate radiotherapy. Four weeks after applying this radiation, 2 symmetrical circular defects with a diameter of 6 mm were created in the parietal bones of each animal. The right-side defect was filled with the materials mentioned above and the left-side defect was not filled (as a control). All defects were covered with a resorbable barrier membrane. During 4 weeks of healing, 1 hour of HBO therapy was applied to the rats in the HBO groups 5 times a week. The rats were then killed, and the calvarial specimens were harvested for radiographic and histologic analyses.
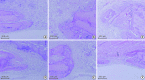
Results: New bone formation was greatest in the FGF-2 subgroup, and improvement was not found in the BCP subgroup. HBO seemed to have a minimal effect on new bone formation. There was tendency for more angiogenesis in the HBO groups than the NHBO groups, but the group with HBO and FGF-2 did not show significantly better outcomes than the HBO-only group or the NHBO group with FGF-2.
Conclusions: HBO exerted beneficial effects on angiogenesis in calvarial defects of irradiated rats over a 4-week healing period, but it appeared to have minimal effects on bone regeneration. FGF-2 seemed to enhance new bone formation and angiogenesis, but its efficacy appeared to be reduced when HBO was applied.
Keywords: Biphasic calcium phosphate; Fibroblast growth factor-2; Hyperbaric oxygen therapy; Radiotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures


References
-
- Anderson L, Meraw S, Al-Hezaimi K, Wang HL. The influence of radiation therapy on dental implantology. Implant Dent. 2013;22:31–38. - PubMed
-
- Granström G, Jacobsson M, Tjellström A. Titanium implants in irradiated tissue: benefits from hyperbaric oxygen. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1992;7:15–25. - PubMed
-
- Jacobsson MG, Jönsson AK, Albrektsson TO, Turesson IE. Short- and long-term effects of irradiation on bone regeneration. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1985;76:841–850. - PubMed
-
- Marx RE. Osteoradionecrosis: a new concept of its pathophysiology. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1983;41:283–288. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

