A new counterintuitive training for adult amblyopia
- PMID: 30847360
- PMCID: PMC6389748
- DOI: 10.1002/acn3.698
A new counterintuitive training for adult amblyopia
Abstract
Objectives: The aim of this study was to investigate whether short-term inverse occlusion, combined with moderate physical exercise, could promote the recovery of visual acuity and stereopsis in a group of adult anisometropic amblyopes.
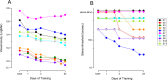
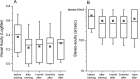
Methods: Ten adult anisometropic patients underwent six brief (2 h) training sessions over a period of 4 weeks. Each training session consisted in the occlusion of the amblyopic eye combined with physical exercise (intermittent cycling on a stationary bike). Visual acuity (measured with ETDRS charts), stereoacuity (measured with the TNO test), and sensory eye dominance (measured with binocular rivalry) were tested before and after each training session, as well as in follow-up visits performed 1 month, 3 months, and 1 year after the end of the training.
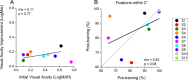
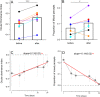
Results: After six brief (2 h) training sessions, visual acuity improved in all 10 patients (0.15 ± 0.02 LogMar), and six of them also recovered stereopsis. The improvement was preserved for up to 1 year after training. A pilot experiment suggested that physical activity might play an important role for the recovery of visual acuity and stereopsis.
Conclusions: Our results suggest a noninvasive training strategy for adult human amblyopia based on an inverse-occlusion procedure combined with physical exercise.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Holmes JM, Clarke MP. Amblyopia. Lancet 2006;367:1343–1351. - PubMed
-
- Levi DM, Carkeet A. Amblyopia: a consequence of abnormal visual development In: Simons K., ed. Early visual development, normal and abnormal. pp. 391–408. New York, NY: Oxford University Press, 1993.
-
- Webber AL, Wood J. Amblyopia: prevalence, natural history, functional effects and treatment. Clin Exp Optom 2005;88:365–375. - PubMed
-
- Berardi N, Pizzorusso T, Maffei L. Critical periods during sensory development. Curr Opin Neurobiol 2000;10:138–145. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

