rt-PA with remote ischemic postconditioning for acute ischemic stroke
- PMID: 30847368
- PMCID: PMC6389851
- DOI: 10.1002/acn3.713
rt-PA with remote ischemic postconditioning for acute ischemic stroke
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the feasibility and safety of remote ischemic postconditioning (RIPC) in acute ischemic stroke patients after intravenous recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (rt-PA) thrombolysis (IVT).
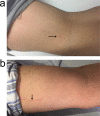
Methods: We performed a pilot randomized trial involving acute ischemic stroke patients with IVT. The patients were randomized 1:1 to receive RIPC or standard medical therapy. In the RIPC group, the participants underwent instant RIPC within 2 h of IVT, followed by repeated RIPC therapy for 7 days. The feasibility end point was the completion of RIPC and time from the first RIPC to finishing IVT in the RIPC group. The safety end point included tissue and neurovascular injury resulting from RIPC, changes in vital signs, level of plasma myoglobin, any hemorrhagic transformation, and other adverse events.
Results: Thirty patients (15 RIPC and 15 Control) were recruited after IVT. The mean age was 65.7 ± 10.2 years, with a National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) score of 6.5 (4.0-10.0). The completion rate for RIPC was 97.0%. The mean time from first RIPC to completing IVT was 66.0 (25.0-75.0) min in the RIPC group. One case of hemorrhagic transformation was observed in the RIPC group. No significant difference was found in the level of myoglobin between the two groups (P > 0.05).
Interpretation: RIPC is effective and safe for AIS patients after intravenous rt-PA thrombolysis.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Xunming Ji is one of the inventors of the electric autocontrol device that has been patented in China (ZL201420846209.5, China). The other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Anderson CS, Robinson T, Lindley RI, et al. Low‐dose versus standard‐dose intravenous alteplase in acute ischemic stroke. N En J Med 2016;374:2313–2323. - PubMed
-
- Hacke W, Kaste M, Bluhmki E, et al. Thrombolysis with alteplase 3 to 4.5 hours after acute ischemic stroke. N En J Med 2008; 359:1317–1329. - PubMed
-
- The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke rt‐PA Stroke Study Group . Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. N En J Med 1995;333:1581–1587. - PubMed
-
- Benarroch EE. Tissue plasminogen activator: beyond thrombolysis. Neurology 2007;69:799–802. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
