Rab25 promotes erlotinib resistance by activating the β1 integrin/AKT/β-catenin pathway in NSCLC
- PMID: 30848009
- PMCID: PMC6536583
- DOI: 10.1111/cpr.12592
Rab25 promotes erlotinib resistance by activating the β1 integrin/AKT/β-catenin pathway in NSCLC
Abstract
Objectives: Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR-TKI) has significant therapeutic efficacy in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. However, acquired resistance is inevitable and limits the long-term efficacy of EGFR-TKI. Our study aimed to investigate the role of ras-associated binding protein 25 (Rab25) in mediating EGFR-TKI resistance in NSCLC.
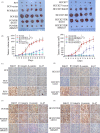
Materials and methods: Rab25 expression in NSCLC patients was measured by immunohistochemical staining. Western blotting was used to analyse the expression of molecules in the Rab25, EGFR and Wnt signalling pathways. Lentiviral vectors were constructed to knock in and knock out Rab25. The biological function of Rab25 was demonstrated by cell-counting kit-8 and flow cytometry. The interaction between Rab25 and β1 integrin was confirmed by co-immunoprecipitation.
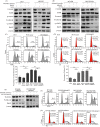
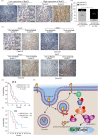
Results: Rab25 overexpression induced erlotinib resistance, whereas Rab25 knockdown reversed this refractoriness in vitro and in vivo. Moreover, Rab25 interacts with β1 integrin and promotes its trafficking to the cytoplasmic membrane. The membrane-β1 integrin induced protein kinase B (AKT) phosphorylation and subsequently activated the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway, promoting cell proliferation. Furthermore, high Rab25 expression was associated with poor response to EGFR-TKI treatment in NSCLC patients.
Conclusions: Rab25 mediates erlotinib resistance by activating the β1 integrin/AKT/β-catenin signalling pathway. Rab25 may be a predictive biomarker and has potential therapeutic value in NSCLC patients with acquired resistance to EGFR-TKI.
Keywords: EGFR-TKI resistance; NSCLC; Rab25; β-catenin; β1 integrin.
© 2019 The Authors Cell Proliferation Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
MCAM interacts with integrin β1 to promote EGFR-TKI resistance in lung adenocarcinoma through the JAK3 signalling pathway.J Transl Med. 2025 Jul 25;23(1):831. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06874-9. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40713600 Free PMC article.
-
PARP1 promotes EGFR-TKI drug-resistance via PI3K/AKT pathway in non-small-cell lung cancer.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2024 Aug;94(2):209-221. doi: 10.1007/s00280-024-04668-2. Epub 2024 Apr 12. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38609654
-
Abnormally activated OPN/integrin αVβ3/FAK signalling is responsible for EGFR-TKI resistance in EGFR mutant non-small-cell lung cancer.J Hematol Oncol. 2020 Dec 7;13(1):169. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-01009-7. J Hematol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33287873 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical rationale for PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway inhibitors as therapy for epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor-resistant non-small-cell lung cancer.Clin Lung Cancer. 2013 Jul;14(4):322-32. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2012.12.001. Epub 2013 Jan 16. Clin Lung Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23332287 Review.
-
Experience with erlotinib in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer.Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2015 Aug;9(4):146-63. doi: 10.1177/1753465815588053. Epub 2015 Jun 10. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2015. PMID: 26063687 Review.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive Analysis of Expression, Clinicopathological Association and Potential Prognostic Significance of RABs in Pancreatic Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 4;21(15):5580. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155580. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32759795 Free PMC article.
-
Claudin1 decrease induced by 1,25-dihydroxy-vitamin D3 potentiates gefitinib resistance therapy through inhibiting AKT activation-mediated cancer stem-like properties in NSCLC cells.Cell Death Discov. 2022 Mar 18;8(1):122. doi: 10.1038/s41420-022-00918-5. Cell Death Discov. 2022. PMID: 35301287 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of ARL4C in Erlotinib Resistance: Activation of the Jak2/Stat 5/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway.Front Oncol. 2020 Oct 28;10:585292. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.585292. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33194732 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of traditional Chinese medicine and epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Aug 7;99(32):e20683. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000020683. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32769861 Free PMC article.
-
Chemotherapeutic drugs: Cell death- and resistance-related signaling pathways. Are they really as smart as the tumor cells?Transl Oncol. 2021 May;14(5):101056. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2021.101056. Epub 2021 Mar 6. Transl Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33684837 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wu YL, Zhou C, Liam CK, et al. First‐line erlotinib versus gemcitabine/cisplatin in patients with advanced EGFR mutation‐positive non‐small‐cell lung cancer: analyses from the phase III, randomized, open‐label, ENSURE study. Ann Oncol. 2015;26:1883‐1889. - PubMed
-
- Rosell R, Carcereny E, Gervais R, et al. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first‐line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation‐positive non‐small‐cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicentre, open‐label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13:239‐246. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

