Comparison of hemodynamic responses and QTc intervals to tracheal intubation with the McGRATH MAC videolaryngoscope and the Macintosh direct laryngoscope in elderly patients
- PMID: 30848023
- PMCID: PMC11900714
- DOI: 10.1002/kjm2.12017
Comparison of hemodynamic responses and QTc intervals to tracheal intubation with the McGRATH MAC videolaryngoscope and the Macintosh direct laryngoscope in elderly patients
Abstract
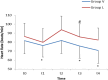
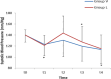
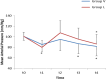
Our hypothesis was that intubations with the McGRATH MAC videolaryngoscope in elderly patients would produce less hemodynamic responses and ECG changes than the Macintosh direct laryngoscope. The patients were divided into two groups: patients who were intubated using the McGRATH MAC (Group V, n = 45) and patients who were intubated using the Macintosh direct laryngoscope (Group L, n = 45). Systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP), mean arterial blood pressure (MAP), heart rate (HR) were recorded before induction with anesthesia (baseline), immediately after induction and at 1 min, 3 min, and 5 min after intubation, with simultaneous ECG. When Group L was compared to Group V, there was an increase in the first, third and fitth minutes after intubation in terms of HR. SBP, MAP increased only at 1 min after intubation and DBP increased in the first and third minutes after intubation in Group L. In Group L, there was a significant difference in the HR values immediately after induction and the first minute after intubation compared with the baseline values. There was a difference in the SBP values immediately after induction and at 3 min and 5 min after intubation compared with the baseline values. There was a difference in DBP and MAP values immediately after induction and at 5 min after intubation. When the McGRATH MAC videolaryngoscope was compared with the Macintosh direct laryngoscope in elderly patients, the McGRATH MAC videolaryngoscope decreased the hemodynamic fluctuations due to tracheal intubation.
Keywords: aged; hemodynamics; intubation; laryngoscopy; videolaryngoscopy.
© 2019 The Authors. Kaohsiung Journal of Medical Sciences published by John Wiley & Sons Australia on behalf of Kaohsiung Medical University.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflicts of interests.
Figures

References
-
- Abdelgawad AF, Shi QF, Halawa MA, Wu ZL, Wu ZY, Chen XD, et al. Comparison of cardiac output and hemodynamic responses of intubation among different videolaryngoscopies in normotensive and hypertensive patients. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technol Med Sci. 2015;35:432–438. - PubMed
-
- Ismail S, Azam SI, Khan FA. Effect of age on haemodynamic response to tracheal intubation. A comparison of young, middle‐aged and elderly patients. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2002;30:608–614. - PubMed
-
- Nakao S, Hatano K, Sumi C, Masuzawa M, Sakamoto S, Ikeda S, et al. Sevoflurane causes greater QTc interval prolongation in elderly patients than in younger patients. Anesth Analg. 2010;110:775–779. - PubMed
-
- Chen YQ, Jin XJ, Liu ZF, Zhu MF. Effects of stellate ganglion block on cardiovascular reaction and heart rate variability in elderly patients during anesthesia induction and endotracheal intubation. J Clin Anesth. 2015;27:140–145. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

