Cortical morphometry of the five-factor model of personality: findings from the Human Connectome Project full sample
- PMID: 30848280
- PMCID: PMC6523439
- DOI: 10.1093/scan/nsz017
Cortical morphometry of the five-factor model of personality: findings from the Human Connectome Project full sample
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to: Cortical morphometry of the five-factor model of personality: findings from the Human Connectome Project full sample.Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2021 Jul 6;16(7):736. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsab036. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33787899 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
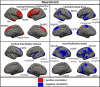
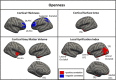
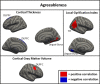
This study is a replication of an existing large study (N = 507) on the surface-based morphometric correlates of five-factor model (FFM) personality traits. The same methods were used as the original study in another large sample drawn from the same population (N = 597) with results then being aggregated from both samples (N = 1104), providing the largest investigation into the neuroanatomical correlates of FFM personality traits to date. Clusters of association between brain morphometry and each FFM trait are reported. For neuroticism, agreeableness, openness and conscientiousness clusters of association were found in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex for at least one morphometric index. Morphometry in various other regions was also associated with each personality trait. While some regions found in the original study were confirmed in the replication and full samples, others were not, highlighting the importance of replicating even high-quality, well-powered studies. Effect sizes were very similar in the replication and whole samples as those found in the original study. As a whole, the current results provide the strongest evidence to date on the neuroanatomical correlates of personality and highlights challenges in using this approach to understanding the neural correlates of personality.
Keywords: MRI; five-factor model; morphometry; personality; traits.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Surface-based morphometry reveals the neuroanatomical basis of the five-factor model of personality.Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2017 Apr 1;12(4):671-684. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsw175. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28122961 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroanatomical correlates of personality traits in temporal lobe epilepsy: Findings from the Epilepsy Connectome Project.Epilepsy Behav. 2019 Sep;98(Pt A):220-227. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2019.07.025. Epub 2019 Aug 3. Epilepsy Behav. 2019. PMID: 31387000 Free PMC article.
-
Robust prediction of individual personality from brain functional connectome.Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2020 May 19;15(3):359-369. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsaa044. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32248238 Free PMC article.
-
No evidence for morphometric associations of the amygdala and hippocampus with the five-factor model personality traits in relatively healthy young adults.PLoS One. 2018 Sep 20;13(9):e0204011. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0204011. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30235257 Free PMC article.
-
Personality traits share overlapping neuroanatomical correlates with internalizing and externalizing psychopathology.J Abnorm Psychol. 2019 Jan;128(1):1-11. doi: 10.1037/abn0000391. Epub 2018 Dec 27. J Abnorm Psychol. 2019. PMID: 30589303
Cited by
-
Mechanical Properties of the Cortex in Older Adults and Relationships With Personality Traits.Hum Brain Mapp. 2025 Feb 1;46(2):e70147. doi: 10.1002/hbm.70147. Hum Brain Mapp. 2025. PMID: 39916406 Free PMC article.
-
Neurite density imaging in amygdala nuclei reveals interindividual differences in neuroticism.Hum Brain Mapp. 2022 Apr 15;43(6):2051-2063. doi: 10.1002/hbm.25775. Epub 2022 Jan 20. Hum Brain Mapp. 2022. PMID: 35049113 Free PMC article.
-
Higher trait neuroticism is associated with greater fatty acid amide hydrolase binding in borderline and antisocial personality disorders.Sci Rep. 2022 Jan 21;12(1):1126. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-04789-9. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35064143 Free PMC article.
-
Association between Reaction Times in the Joint Simon Task and Personality Traits.Brain Sci. 2023 Aug 15;13(8):1207. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13081207. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 37626563 Free PMC article.
-
An fMRI investigation of the relations between Extraversion, internalizing psychopathology, and neural activation following reward receipt in the Human Connectome Project sample.Personal Neurosci. 2020 Nov 24;3:e13. doi: 10.1017/pen.2020.11. eCollection 2020. Personal Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33354651 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allen T.A., DeYoung C.G. (2015). Personality neuroscience and the five factor model In: Oxford Handbook of the Five Factor Model. New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
-
- Behrmann M., Geng J.J., Shomstein S. (2004). Parietal cortex and attention. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 14, 212–217. - PubMed
-
- Berlim M.T., Van Den Eynde F., Tovar-Perdomo S., Daskalakis Z.J. (2014). Response, remission and drop-out rates following high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) for treating major depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized, double-blind and sham-controlled trials. Psychological Medicine, 44, 225–239. - PubMed
-
- Brunoni A.R., Chaimani A., Moffa A.H., et al. (2017). Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for the acute treatment of major depressive episodes a systematic review with network meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry, 74, 143–152. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

