De Novo Designed Amphipathic α-Helical Antimicrobial Peptides Incorporating Dab and Dap Residues on the Polar Face To Treat the Gram-Negative Pathogen, Acinetobacter baumannii
- PMID: 30848594
- PMCID: PMC6886721
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b01785
De Novo Designed Amphipathic α-Helical Antimicrobial Peptides Incorporating Dab and Dap Residues on the Polar Face To Treat the Gram-Negative Pathogen, Acinetobacter baumannii
Abstract
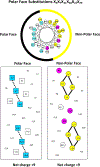
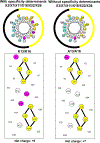
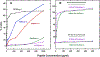
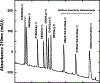
We have designed de novo and synthesized ten 26-residue D-conformation amphipathic α-helical cationic antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), seven with "specificity determinants", which provide specificity for prokaryotic cells over eukaryotic cells. The ten AMPs contain five or six positively charged residues (d-Arg, d-Lys, d-Orn, l-Dab, or l-Dap) on the polar face to understand their role in hemolytic activity against human red blood cells and antimicrobial activity against seven Acinetobacter baumannii strains, resistant to polymyxin B and colistin, and 20 A. baumannii worldwide isolates from 2016 and 2017 with antibiotic resistance to 18 different antibiotics. AMPs with specificity determinants and with l-Dab and l-Dap residues on the polar face have essentially no hemolytic activity at 1000 μg/mL (380 μM), showing for the first time the importance of these unusual amino acid residues in solving long-standing hemolysis issues of AMPs. Specificity determinants maintained excellent antimicrobial activity in the presence of human sera.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of positively charged residues on the polar and non-polar faces of amphipathic α-helical antimicrobial peptides on specificity and selectivity for Gram-negative pathogens.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2018 Jan;91(1):75-92. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.13058. Epub 2017 Jul 14. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2018. PMID: 28636788
-
Design of Novel Amphipathic α-Helical Antimicrobial Peptides with No Toxicity as Therapeutics against the Antibiotic-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacterial Pathogen, Acinetobacter Baumannii.J Med Chem Drug Des. 2019;2(2):114. Epub 2019 May 30. J Med Chem Drug Des. 2019. PMID: 34377965 Free PMC article.
-
Design of imperfectly amphipathic α-helical antimicrobial peptides with enhanced cell selectivity.Acta Biomater. 2014 Jan;10(1):244-57. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2013.08.043. Epub 2013 Sep 8. Acta Biomater. 2014. PMID: 24021230
-
Antimicrobial peptides as a promising treatment option against Acinetobacter baumannii infections.Microb Pathog. 2020 Sep;146:104238. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2020.104238. Epub 2020 May 5. Microb Pathog. 2020. PMID: 32387392 Review.
-
Impact of chemical modifications on the antimicrobial and hemolytic activity of helical amphipathic peptide Lasioglossin LL-III.Amino Acids. 2023 Nov;55(11):1531-1544. doi: 10.1007/s00726-023-03326-w. Epub 2023 Sep 22. Amino Acids. 2023. PMID: 37737904 Review.
Cited by
-
Dimerization and lysine substitution of melittin have differing effects on bacteria.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Oct 7;15:1443497. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1443497. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39434904 Free PMC article.
-
Challenge in the Discovery of New Drugs: Antimicrobial Peptides against WHO-List of Critical and High-Priority Bacteria.Pharmaceutics. 2021 May 21;13(6):773. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13060773. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34064302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of substituting glutamine with lysine on structural and biological properties of antimicrobial peptide Polybia-MP1.Amino Acids. 2023 Jul;55(7):881-890. doi: 10.1007/s00726-023-03276-3. Epub 2023 Jun 10. Amino Acids. 2023. PMID: 37300579
-
The effects of incorporation of the counterparts and mimics of L-lysine on the antimicrobial activity, hemolytic activity, cytotoxicity and tryptic stability of antimicrobial peptide polybia-MPII.Amino Acids. 2022 Jan;54(1):123-135. doi: 10.1007/s00726-021-03099-0. Epub 2021 Nov 26. Amino Acids. 2022. PMID: 34825276
-
Rescuing humanity by antimicrobial peptides against colistin-resistant bacteria.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022 Jun;106(11):3879-3893. doi: 10.1007/s00253-022-11940-z. Epub 2022 May 23. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35604438 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Coast J; Smith RD; Millar MR Superbugs: should antimicrobial resistance be included as a cost in economic evaluation? Health Econ. 1996, 5, 217–226. - PubMed
-
- Laxminarayan R; Duse A; Wattal C; Zaidi AKM; Wertheim HFL; Sumpradit N; Vlieghe E; Hara GL; Gould IM; Goossens H; Greko C; So AD; Bigdeli M; Tomson G; Woodhouse W; Ombaka E; Peralta AQ; Qamar FN; Mir F; Kariuki S; Bhutta ZA; Coates A; Bergstrom R; Wright GD; Brown ED; Cars O Antibiotic resistance-the need for global solutions. Lancet Infect. Dis 2013, 13, 1057–1098. - PubMed
-
- Uggerhoj LE; Poulsen TJ; Munk JK; Fredborg M; Sondergaard TE; Frimodt-Moller N; Hansen RP; Wimmer R Rational design of alpha-helical antimicrobial peptides: Do’s and Don’ts. ChemBioChem 2015, 16, 242–253. - PubMed
-
- Wieprecht T; Dathe M; Krause E; Beyermann M; Maloy WL; MacDonald DL; Bienert M Modulation of membrane activity of amphipathic, antibacterial peptides by slight modifications of the hydrophobic moment. FEBS Lett. 1997, 417, 135–140. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

