Genetic and genomic evidence for an important role of the Na+/H+ exchanger 3 in blood pressure regulation and angiotensin II-induced hypertension
- PMID: 30849009
- PMCID: PMC6485378
- DOI: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00122.2018
Genetic and genomic evidence for an important role of the Na+/H+ exchanger 3 in blood pressure regulation and angiotensin II-induced hypertension
Abstract
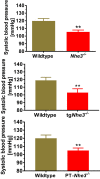
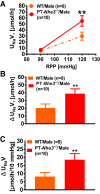
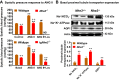
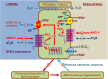
The sodium (Na+)/hydrogen (H+) exchanger 3 (NHE3) and sodium-potassium adenosine triphosphatase (Na+/K+-ATPase) are two of the most important Na+ transporters in the proximal tubules of the kidney. On the apical membrane side, NHE3 primarily mediates the entry of Na+ into and the exit of H+ from the proximal tubules, directly and indirectly being responsible for reabsorbing ~50% of filtered Na+ in the proximal tubules of the kidney. On the basolateral membrane side, Na+/K+-ATPase serves as a powerful engine driving Na+ out of, while pumping K+ into the proximal tubules against their concentration gradients. While the roles of NHE3 and Na+/K+-ATPase in proximal tubular Na+ transport under in vitro conditions are well recognized, their respective contributions to the basal blood pressure regulation and angiotensin II (ANG II)-induced hypertension remain poorly understood. Recently, we have been fortunate to be able to use genetically modified mouse models with global, kidney- or proximal tubule-specific deletion of NHE3 to directly determine the cause and effect relationship between NHE3, basal blood pressure homeostasis, and ANG II-induced hypertension at the whole body, kidney and/or proximal tubule levels. The purpose of this article is to review the genetic and genomic evidence for an important role of NHE3 with a focus in the regulation of basal blood pressure and ANG II-induced hypertension, as we learned from studies using global, kidney- or proximal tubule-specific NHE3 knockout mice. We hypothesize that NHE3 in the proximal tubules is necessary for maintaining basal blood pressure homeostasis and the development of ANG II-induced hypertension.
Keywords: NHE3; angiotensin II; hypertension; intestines; kidney; proximal tubule.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Proximal Tubule-Specific Deletion of the NHE3 (Na+/H+ Exchanger 3) in the Kidney Attenuates Ang II (Angiotensin II)-Induced Hypertension in Mice.Hypertension. 2019 Sep;74(3):526-535. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.119.13094. Epub 2019 Jul 29. Hypertension. 2019. PMID: 31352824 Free PMC article.
-
New Insights into the Critical Importance of Intratubular Na+/H+ Exchanger 3 and Its Potential Therapeutic Implications in Hypertension.Curr Hypertens Rep. 2021 Jun 10;23(6):34. doi: 10.1007/s11906-021-01152-7. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2021. PMID: 34110521 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Na+/H+ Exchanger 3 in the Intestines and the Proximal Tubule of the Kidney: Localization, Physiological Function, and Key Roles in Angiotensin II-Induced Hypertension.Front Physiol. 2022 Apr 19;13:861659. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.861659. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35514347 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic Deletion of AT1a Receptor or Na+/H+ Exchanger 3 Selectively in the Proximal Tubules of the Kidney Attenuates Two-Kidney, One-Clip Goldblatt Hypertension in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 13;23(24):15798. doi: 10.3390/ijms232415798. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555438 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin II and AT1a Receptors in the Proximal Tubules of the Kidney: New Roles in Blood Pressure Control and Hypertension.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 22;23(5):2402. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052402. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35269547 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Proximal Tubule-Specific Deletion of the NHE3 (Na+/H+ Exchanger 3) in the Kidney Attenuates Ang II (Angiotensin II)-Induced Hypertension in Mice.Hypertension. 2019 Sep;74(3):526-535. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.119.13094. Epub 2019 Jul 29. Hypertension. 2019. PMID: 31352824 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk between Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter Inhibitors and Sodium-Hydrogen Exchanger 1 and 3 in Cardiometabolic Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 24;22(23):12677. doi: 10.3390/ijms222312677. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34884494 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiotensin III/AT2 Receptor/NHE3 Signaling Pathway in the Proximal Tubules of the Kidney: A Novel Natriuretic and Antihypertensive Mechanism in Hypertension.J Am Heart Assoc. 2019 May 7;8(9):e012644. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.012644. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019. PMID: 31039655 Free PMC article.
-
Expression Regulation of Water Reabsorption Genes and Transcription Factors in the Kidneys of Lepus yarkandensis.Front Physiol. 2022 May 26;13:856427. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.856427. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35721542 Free PMC article.
-
New Insights into the Critical Importance of Intratubular Na+/H+ Exchanger 3 and Its Potential Therapeutic Implications in Hypertension.Curr Hypertens Rep. 2021 Jun 10;23(6):34. doi: 10.1007/s11906-021-01152-7. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2021. PMID: 34110521 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- ALLHAT Officers and Coordinators for the ALLHAT Collaborative Research Group. The Antihypertensive and Lipid-Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial Major outcomes in high-risk hypertensive patients randomized to angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or calcium channel blocker vs diuretic: The Antihypertensive and Lipid-Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial (ALLHAT). JAMA 288: 2981–2997, 2002. doi:10.1001/jama.288.23.2981. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

