Is there a fundamental flaw in Canada's post-arrival immigrant surveillance system for tuberculosis?
- PMID: 30849130
- PMCID: PMC6407769
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0212706
Is there a fundamental flaw in Canada's post-arrival immigrant surveillance system for tuberculosis?
Abstract
Background: New immigrants to Canada with a history of tuberculosis or evidence of old healed tuberculosis on chest radiograph are referred to public health authorities for medical surveillance. This ostensible public health protection measure identifies a subgroup of patients (referrals) who are at very low risk (compared to non-referrals) of transmission.
Methods: To assess whether earlier diagnosis or a different phenotypic expression of disease explains this difference, we systematically reconstructed the immigration and transmission histories from a well-defined cohort of recently-arrived referral and non-referral pulmonary tuberculosis cases in Canada. Incident case chest radiographs in all cases and sequential past radiographs in referrals were re-read by three experts. Change in disease severity from pre-immigration radiograph to incident radiograph was the primary, and transmission of tuberculosis, the secondary, outcome.
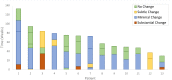
Results: There were 174 cohort cases; 61 (35.1%) referrals and 113 (64.9%) non-referrals. Compared to non-referrals, referrals were less likely to be symptomatic (26% vs. 80%), smear-positive (15% vs. 50%), or to have cavitation (0% vs. 35%) or extensive disease (15% vs. 59%) on chest radiograph. After adjustment for referral status, time between films, country-of-birth, age and co-morbidities, referrals were less likely to have substantial changes on chest radiograph; OR 0.058 (95% CI 0.018-0.199). All secondary cases and 82% of tuberculin skin test conversions occurred in contacts of non-referrals.
Conclusions: Phenotypically different disease, and not earlier diagnosis, explains the difference in transmission risk between referrals and non-referrals. Screening, and treating high-risk non-referrals for latent tuberculosis is necessary to eliminate tuberculosis in Canada.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Department of Pensions and National Health, Canada. Immigration Medical Service. Medical Examination of Immigrants Instructions to Medical Officers. Ottawa, Canada; 1931.
-
- Department of National Health and Welfare. Immigration Medical Service. Medical Services Manual of Instructions to Medical Officers. 1959.
-
- U.S. Department of Health, Education and Welfare. Public Health Services Manual for Medical Examination of Aliens. Washington, USA; 1963.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

