Ghrelin regulation of glucose metabolism
- PMID: 30849212
- PMCID: PMC6688917
- DOI: 10.1111/jne.12705
Ghrelin regulation of glucose metabolism
Abstract
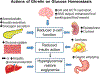
Ghrelin and its receptor, the growth hormone secretagogue receptor 1a (GHSR1a), are implicated in the regulation of glucose metabolism via direct actions in the pancreatic islet, as well as peripheral insulin-sensitive tissues and the brain. Although many studies have explored the role of ghrelin in glucose tolerance and insulin secretion, a complete mechanistic understanding remains to be clarified. This review highlights the local expression and function of ghrelin and GHSR1a in pancreatic islets and how this axis may modulate insulin secretion from pancreatic β-cells. Additionally, we discuss the effect of ghrelin on in vivo glucose metabolism in rodents and humans, as well as the metabolic circumstances under which the action of ghrelin may predominate.
Keywords: ghrelin; glucose tolerance; insulin; insulin secretion.
© 2019 British Society for Neuroendocrinology.
Figures
References
-
- Kojima M, Hosoda H, Date Y, Nakazato M, Matsuo H, Kangawa K. Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature. 1999; 402(6762): 656. - PubMed
-
- Müller TD, Nogueiras R, Andermann ML, Andrews ZB, Anker SD, Argente J, Batterham RL, Benoit SC, Bowers CY, Broglio F, Casanueva FF, D’Alessio D, Depoortere I, Geliebter A, Ghigo E, Cole PA, Cowley M, Cummings DE, Dagher A, Diano S, Dickson SL, Diéguez C, Granata R, Grill HJ, Grove K, Habegger KM, Heppner K, Heiman ML, Holsen L, Holst B, Inui A, Jansson JO, Kirchner H, Korbonits M, Laferrère B, LeRoux CW, Lopez M, Morin S, Nakazato M, Nass R, Perez-Tilve D, Pfluger PT, Schwartz TW, Seeley RJ, Sleeman M, Sun Y, Sussel L, Tong J, Thorner MO, van der Lely AJ, van der Ploeg LHT, Zigman JM, Kojima M, Kangawa K, Smith RG, Horvath T, Tschöp MH. Ghrelin. Molecular Metabolism 2015; 4(6): 437–60. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Virdis A, Lerman LO, Regoli F, Ghiadoni L, Lerman A, Taddei S. Human Ghrelin: A Gastric Hormone with Cardiovascular Properties. Curr Pharm Des 2016; 22(1): 52–8. - PubMed
-
- Goldstein J, Zhao T-J, Li R, Sherbet D, Liang G, Brown M. Surviving starvation: essential role of the ghrelin-growth hormone axis. Cold Spring Harbor symposia on quantitative biology, 2011. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

