Expression and clinical significance of PD-L1, B7-H3, B7-H4 and TILs in human small cell lung Cancer (SCLC)
- PMID: 30850021
- PMCID: PMC6408760
- DOI: 10.1186/s40425-019-0540-1
Expression and clinical significance of PD-L1, B7-H3, B7-H4 and TILs in human small cell lung Cancer (SCLC)
Abstract
Background: Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) accounts for 10-15% of all lung malignancies and its prognosis is dismal. Although early studies have shown promising clinical activity of immune checkpoint blockers, the immune composition and expression of potentially actionable immunostimulatory targets in this malignancy are poorly understood.
Methods: Using multiplexed quantitative immunofluorescence (QIF), we measured the levels of 3 different B7 family ligands PD-L1, B7-H3, B7-H4 and major tumor infiltrating lymphocyte (TIL) subsets in 90 SCLC samples represented in tissue microarray format. Associations between the marker levels, clinicopathological variables and survival were studied.
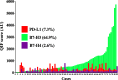
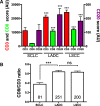
Results: PD-L1 protein was detected in 7.3%, B7-H3 in 64.9% and B7-H4 in 2.6% of SCLC cases. The markers showed limited co-expression and were not associated with the level of TILs, age, gender and stage. Elevated B7-H4 was associated with shorter 5-year overall survival. The levels of CD3+, CD8+ and CD20+ TILs and the ratio of total/effector T-cells were significantly lower in SCLC than in non-small cell lung cancer. High levels of CD3+, but not CD8+ or CD20+ TILs were significantly associated with longer survival.
Conclusions: Taken together, our study indicate variable expression and clinical role of B7-family ligands in SCLC with predominant expression of the candidate target B7-H3 and the presence of a limited cytotoxic anti-tumor immune response. These results support the evaluation of B7-H3 blockers and/or pro-inflammatory therapies in SCLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All tissue was used after approval from the Yale Human Investigation Committee protocols #9505008219 and #1608018220, which approved the patient consent forms or in some cases waiver of consent.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
Kurt Schalper: Consultant or advisor for Celgene, Moderna Therapeutics, Shattuck Labs, AstraZeneca, Pierre-Fabre and Abbvie. Research funding by Navigate Biopharma, Vasculox/Tioma, Tesaro, Takeda, Moderna Therapeutics, Surface Oncology, Pierre-Fabre, Merck and Bristol-Myers Squibb.
David Rimm: Consultant or advisor for Amgen, AstraZeneca, Agendia, Biocept, BMS, Cell Signaling Technology, Cepheid, Daiichi Sankyo, GSK, InVicro/Konica/ Minolta, Merck, NanoString, Perkin Elmer, PAIGE.AI, and Ultivue. Equity holder in PixelGear (start-up company related to direct tissue imaging) Research funding from AstraZeneca, Cepheid, Navigate/Novartis, NextCure, Lilly, Ultivue, Ventana and Perkin Elmer/Akoya.
Mehmet Altan: Research funding from BMS and Lilly.
Vamsidhar Velcheti: Consultant or advisory role for Genentech, BMS, AstraZeneca, Merck, Nektar therapeutics, Reddy Labs, Celgene, Foundation Medicine and Takeda Oncology.
Roy Herbst: Consultant or advisory role for Abbvie Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, Biodesix, Bristol-Myers Squibb , Eli Lilly and Company, EMD Serono, Genentech/Roche, Heat Biologics, Loxo Oncology, Merck and Company, Nektar, NextCure, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, Seattle Genetics, Shire PLC, Spectrum Pharmaceuticals, Symphogen, Tesaro, Neon Therapeutics, Infinity Pharmaceuticals. Research support from AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly and Company, Merck and Company. Member of the board of directors (non-executive/ independent) for Junshi Pharmaceuticals.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures




References
-
- Arcaro A. Targeted therapies for small cell lung cancer: Where do we stand? Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2015;95(2):154-64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
