Community exercise is feasible for neuromuscular diseases and can improve aerobic capacity
- PMID: 30850441
- PMCID: PMC6511083
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000007265
Community exercise is feasible for neuromuscular diseases and can improve aerobic capacity
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this phase 2 trial was to ascertain the feasibility and effect of community-based aerobic exercise training for people with 2 of the more common neuromuscular diseases: Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1A (CMT) and inclusion body myositis (IBM).
Methods: A randomized single-blinded crossover trial design was used to compare a 12-week aerobic training program using recombinant exercise bicycles compared to a control period. The training occurred 3 times per week in community gyms local to the participants. Support was available from trained gym staff and a research physiotherapist. The 2 disease groups were analyzed separately. The primary outcome measure was peak oxygen uptake (VO2 peak) during a maximal exercise test, with secondary measures of muscle strength, function, and patient-reported measures.
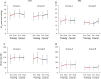
Results: Data from 23 people with CMT and 17 people with IBM were included in the analysis. Both disease groups had high levels of participation and demonstrated improvements in VO2 peak, with a moderate effect size in the CMT participants (Cohen d = 0.53) and a strong effect size in the IBM group (Cohen d = 1.72). No major changes were observed in the secondary outcome measures. Qualitative interviews revealed that participants valued the support of gym instructors and the research physiotherapists in overcoming challenges to participation.
Conclusion: Twelve weeks of aerobic training in community gyms was feasible, safe, and improved aerobic capacity in people with CMT and IBM.
Classification of evidence: This study provides Class II evidence that for patients with CMT type 1A and IBM, an aerobic training program increases aerobic capacity.
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the American Academy of Neurology.
Figures

References
-
- Anens E, Emtner M, Hellström K. Exploratory study of physical activity in persons with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2015;96:260–268. - PubMed
-
- Kalkman JS, Schillings ML, Zwarts MJ, van Engelen BG, Bleijenberg G. The development of a model of fatigue in neuromuscular disorders: a longitudinal study. J Psychosom Res 2007;62:571–579. - PubMed
-
- Carter GT, Abresch RT, Fowler WMJ, Johnson ER, Kilmer DD, McDonald CM. Profiles of neuromuscular diseases: hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy, types I and II. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 1995;74:S140–S149. - PubMed
-
- Wiesinger GF, Quittan M, Nuhr M, Volc-Platzer G, Zehetgruber M, Graninger W. Aerobic capacity in adult dermatomyositis/polymyositis patients and healthy controls. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2000;81:1–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
