Cholecystokinin release triggered by NMDA receptors produces LTP and sound-sound associative memory
- PMID: 30850520
- PMCID: PMC6442640
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1816833116
Cholecystokinin release triggered by NMDA receptors produces LTP and sound-sound associative memory
Abstract
Memory is stored in neural networks via changes in synaptic strength mediated in part by NMDA receptor (NMDAR)-dependent long-term potentiation (LTP). Here we show that a cholecystokinin (CCK)-B receptor (CCKBR) antagonist blocks high-frequency stimulation-induced neocortical LTP, whereas local infusion of CCK induces LTP. CCK-/- mice lacked neocortical LTP and showed deficits in a cue-cue associative learning paradigm; and administration of CCK rescued associative learning deficits. High-frequency stimulation-induced neocortical LTP was completely blocked by either the NMDAR antagonist or the CCKBR antagonist, while application of either NMDA or CCK induced LTP after low-frequency stimulation. In the presence of CCK, LTP was still induced even after blockade of NMDARs. Local application of NMDA induced the release of CCK in the neocortex. These findings suggest that NMDARs control the release of CCK, which enables neocortical LTP and the formation of cue-cue associative memory.
Keywords: NMDA receptor; cholecystokinin; entorhinal cortex; long-term potentiation; memory.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


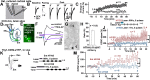
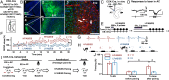
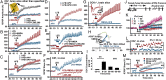

References
-
- Kandel ER. The molecular biology of memory storage: A dialogue between genes and synapses. Science. 2001;294:1030–1038. - PubMed
-
- Artola A, Singer W. Long-term potentiation and NMDA receptors in rat visual cortex. Nature. 1987;330:649–652. - PubMed
-
- Lomo T. Potentiation of monosynaptic EPSPs in the perforant path-dentate granule cell synapse. Exp Brain Res. 1971;12:46–63. - PubMed
-
- Bliss TV, Collingridge GL. A synaptic model of memory: Long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature. 1993;361:31–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

