Divergent patterns of TDP-43 and tau pathologies in primary progressive aphasia
- PMID: 30851133
- PMCID: PMC6538935
- DOI: 10.1002/ana.25465
Divergent patterns of TDP-43 and tau pathologies in primary progressive aphasia
Abstract
Objective: To measure postmortem burden of frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD) with TDP-43 (FTLD-TDP) or tau (FTLD-Tau) proteinopathy across hemispheres in primary progressive aphasia (PPA) using digital histopathology and to identify clinicopathological correlates of these distinct proteinopathies.
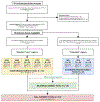
Methods: In an autopsy cohort of PPA (FTLD-TDP = 13, FTLD-Tau = 14), we analyzed laterality and regional distribution of postmortem pathology, quantified using a validated digital histopathological approach, in available brain tissue from up to 8 cortical regions bilaterally. We related digital pathology to antemortem structural neuroimaging and specific clinical language features.
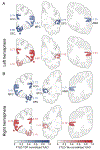
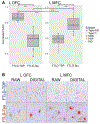
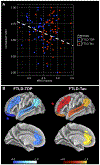
Results: Postmortem cortical pathology was left-lateralized in both FTLD-TDP (beta = -0.15, standard error [SE] = 0.05, p = 0.007) and FTLD-Tau (beta = -0.09, SE = 0.04, p = 0.015), but the degree of lateralization decreased with greater overall dementia severity before death (beta = -8.18, SE = 3.22, p = 0.015). Among 5 core pathology regions sampled, we found greatest pathology in left orbitofrontal cortex (OFC) in FTLD-TDP, which was greater than in FTLD-Tau (F = 47.07, df = 1,17, p < 0.001), and in left midfrontal cortex (MFC) in FTLD-Tau, which was greater than in FTLD-TDP (F = 19.34, df = 1,16, p < 0.001). Postmortem pathology was inversely associated with antemortem magnetic resonance imaging cortical thickness (beta = -0.04, SE = 0.01, p = 0.007) in regions matching autopsy sampling. Irrespective of PPA syndromic variant, single-word comprehension impairment was associated with greater left OFC pathology (t = -3.72, df = 10.72, p = 0.004) and nonfluent speech with greater left MFC pathology (t = -3.62, df = 12.00, p = 0.004) among the 5 core pathology regions.
Interpretation: In PPA, FTLD-TDP and FTLD-Tau have divergent anatomic distributions of left-lateralized postmortem pathology that relate to antemortem structural imaging and distinct language deficits. Although other brain regions may be implicated in neural networks supporting these complex language measures, our observations may eventually help to improve antemortem diagnosis of neuropathology in PPA. Ann Neurol 2019;85:630-643.
© 2019 American Neurological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential Conflicts of Interest
Nothing to report.
Figures


References
-
- Mesulam MM. Primary progressive aphasia. Ann. Neurol 2001;49(4):425–432. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

