Obstacles to Scanning by RNase E Govern Bacterial mRNA Lifetimes by Hindering Access to Distal Cleavage Sites
- PMID: 30852060
- PMCID: PMC6541411
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.01.044
Obstacles to Scanning by RNase E Govern Bacterial mRNA Lifetimes by Hindering Access to Distal Cleavage Sites
Abstract
The diversity of mRNA lifetimes in bacterial cells is difficult to reconcile with the relaxed cleavage site specificity of RNase E, the endonuclease most important for governing mRNA degradation. This enzyme has generally been thought to locate cleavage sites by searching freely in three dimensions. However, our results now show that its access to such sites in 5'-monophosphorylated RNA is hindered by obstacles-such as bound proteins or ribosomes or coaxial small RNA (sRNA) base pairing-that disrupt the path from the 5' end to those sites and prolong mRNA lifetimes. These findings suggest that RNase E searches for cleavage sites by scanning linearly from the 5'-terminal monophosphate along single-stranded regions of RNA and that its progress is impeded by structural discontinuities encountered along the way. This discovery has major implications for gene regulation in bacteria and suggests a general mechanism by which other prokaryotic and eukaryotic regulatory proteins can be controlled.
Keywords: 5′ terminus; RNA decay; RNA processing; RNase G; SgrS; phosphosugar stress; ribonuclease; ribosome; uORF; yigL.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
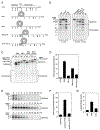

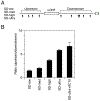
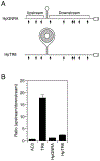

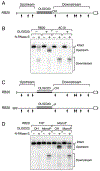
References
-
- Antson AA, Dodson EJ, Dodson G, Greaves RB, Chen X, and Gollnick P (1999). Structure of the trp RNA-binding attenuation protein, TRAP, bound to RNA. Nature 401, 235–242. - PubMed
-
- Båga M, Göransson M, Normark S, and Uhlin BE (1988). Processed mRNA with differential stability in the regulation of E. coli pilin gene expression. Cell 52, 197–206. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

