Cascade Signals of Papaverine Inhibiting LPS-Induced Retinal Microglial Activation
- PMID: 30852743
- PMCID: PMC6453874
- DOI: 10.1007/s12031-019-01289-w
Cascade Signals of Papaverine Inhibiting LPS-Induced Retinal Microglial Activation
Abstract
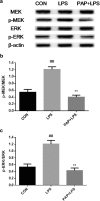
Studies have shown that papaverine can inhibit lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced microglial activation. The retinal primary microglia of newborn SD rats were isolated and purified, and a LPS-induced microglia activation model was established. The protein phosphorylation level of the signaling pathway was detected by western blotting. The transcription and expression of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-10 were respectively detected by RT-PCR and ELISA to observe the abnormal activation of primary microglia. The cAMP inhibitor Rp-isomer, PKA inhibitor H89, and MEK inhibitor U0126 were separately added to further investigate the role of MEK/Erk in PAP inhibition of primary microglial activation and the relationship between cAMP/PKA and MEK/Erk. It was found that the level of MEK phosphorylation was upregulated after LPS stimulation, which was blocked by 10 μg/ml of papaverine.10μM U0126 significantly inhibited TNF-α and IL-1β and increased IL-10 transcription and expression in retinal microglia (P < 0.01). Both Rp-isomer and H89 upregulated the phosphorylation levels of MEK and Erk. Papaverine may inhibit inflammatory factors and promote the expression of anti-inflammatory factors through the cAMP/PKA and MEK/Erk pathway, thereby inhibiting LPS-induced activation of primary retinal microglia, and the MEK/Erk pathway may be partially regulated by cAMP/PKA, which can provide theoretical basis and experimental basis for its protection of the central nervous system.
Keywords: MEK/Erk; Papaverine; Primary microglia; cAMP/PKA.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Figures






Similar articles
-
The phosphodiesterase 10 inhibitor papaverine exerts anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects via the PKA signaling pathway in neuroinflammation and Parkinson's disease mouse models.J Neuroinflammation. 2019 Dec 2;16(1):246. doi: 10.1186/s12974-019-1649-3. J Neuroinflammation. 2019. PMID: 31791357 Free PMC article.
-
Xenon enhances LPS-induced IL-1β expression in microglia via the extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 pathway.J Mol Neurosci. 2011 Sep;45(1):48-59. doi: 10.1007/s12031-010-9432-z. Epub 2010 Aug 3. J Mol Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 20680516
-
Naloxone inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced activation of retinal microglia is partly mediated via the p38 mitogen activated protein kinase signalling pathway.J Int Med Res. 2012;40(4):1438-48. doi: 10.1177/147323001204000422. J Int Med Res. 2012. PMID: 22971495
-
Minocycline inhibits LPS-induced retinal microglia activation.Neurochem Int. 2005 Jul;47(1-2):152-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2005.04.018. Neurochem Int. 2005. PMID: 15904993
-
Morphine mediates a proinflammatory phenotype via μ-opioid receptor-PKCɛ-Akt-ERK1/2 signaling pathway in activated microglial cells.Biochem Pharmacol. 2013 Aug 15;86(4):487-96. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2013.05.027. Epub 2013 Jun 21. Biochem Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23796752
Cited by
-
Papaverine: A Miraculous Alkaloid from Opium and Its Multimedicinal Application.Molecules. 2023 Mar 31;28(7):3149. doi: 10.3390/molecules28073149. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37049912 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unraveling the Nephroprotective Potential of Papaverine against Cisplatin Toxicity through Mitigating Oxidative Stress and Inflammation: Insights from In Silico, In Vitro, and In Vivo Investigations.Molecules. 2024 Apr 23;29(9):1927. doi: 10.3390/molecules29091927. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38731418 Free PMC article.
-
Repurposing Papaverine as an Antiviral Agent against Influenza Viruses and Paramyxoviruses.J Virol. 2020 Feb 28;94(6):e01888-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01888-19. Print 2020 Feb 28. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 31896588 Free PMC article.
-
The phosphodiesterase 10 inhibitor papaverine exerts anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects via the PKA signaling pathway in neuroinflammation and Parkinson's disease mouse models.J Neuroinflammation. 2019 Dec 2;16(1):246. doi: 10.1186/s12974-019-1649-3. J Neuroinflammation. 2019. PMID: 31791357 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bhat NR, Zhang P, Lee JC, Hogan EL. Extracellular signal-regulated kinase and p38 subgroups of mitogen-activated protein kinases regulate inducible nitric oxide synthase and tumor necrosis factor-α gene expression in endotoxin-stimulated primary glial cultures. J Neurosci. 1998;18(5):1633–1641. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-05-01633.1998. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Buttini M, Mir A, Appel K, Wiederhold KH, Limonta S, Gebicke-Haerter PJ, Boddeke HWGM. Lipopolysaccharide induces expression of tumour necrosis factor alpha in rat brain: inhibition by methylprednisolone and by rolipram. Br J Pharmacol. 1997;122:1483–1489. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0701502. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

