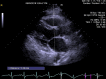
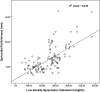
Epicardial fat thickness is significantly increased and related to LDL cholesterol level in patients with familial hypercholesterolemia
- PMID: 30852775
- PMCID: PMC6704218
- DOI: 10.1007/s40477-019-00368-3
Epicardial fat thickness is significantly increased and related to LDL cholesterol level in patients with familial hypercholesterolemia
Abstract
Purpose: Increased epicardial fat thickness (EFT) is accepted as a risk factfcardiovascular diseases in some studies. There are conflicting results about the relation between plasma low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) level and EFT. As well, the relation between EFT and familial hypercholesterolemia is not clearly documented in the literature. Our aim was to investigate EFT in familial hypercholesterolemia patients and to determine which parameters were related to EFT increase.
Methods: A total of 150 subjects enrolled in our study. Subjects were separated into two groups: 75 hypercholesterolemia patients (16 men, mean age 52.8 ± 7.4 years) and 75 familial hypercholesterolemia patients (26 men, mean age 50.7 ± 9.2 years). Medical history assessments and complete physical examinations were done. Routine laboratory tests and echocardiographic measurements were performed.
Results: Coronary artery disease frequency was significantly higher in the familial hypercholesterolemia group (p < 0.001). This group had significantly higher TC and LDL-C levels than the hypercholesterolemia group (p < 0.05 for all). EFT values were higher in the familial hypercholesterolemia group, and were significantly different than in the other group (p < 0.001). LDL-C was found to be independently related to EFT in the linear regression analysis.
Conclusions: Epicardial fat thickness increased in the familial hypercholesterolemia patients. In addition, LDL-C levels were significantly crelated with increased EFT.
Keywords: Epicardial fat thickness; Familial hypercholesterolemia.
Conflict of interest statement
The auths declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Sacks HS, Fain JN, Cheema P, Bahouth SW, Garrett E, Wolf RY, et al. Inflammatory genes in epicardial fat contiguous with coronary atherosclerosis in the metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes: changes associated with pioglitazone. Diabetes Care. 2011;34:730–733. doi: 10.2337/dc10-2083. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials