Long-Term Efficacy of Mirabegron Add-On Therapy to Antimuscarinic Agents in Patients With Spinal Cord Injury
- PMID: 30852871
- PMCID: PMC6409660
- DOI: 10.5535/arm.2019.43.1.54
Long-Term Efficacy of Mirabegron Add-On Therapy to Antimuscarinic Agents in Patients With Spinal Cord Injury
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the long-term efficacy of mirabegron add-on therapy in patients with spinal cord injury (SCI) based on an urodynamic study.
Methods: This retrospective study involved a chart audit of individuals with SCI who underwent two consecutive urodynamic studies between April 1, 2015 and April 1, 2018. After adding 50 mg of mirabegron once a day to the pre-existing antimuscarinic therapy for a period of, at least 6 months, the following variables were analyzed: change in cystometric capacity, change in bladder compliance, change in maximal detrusor pressure, change in reflex volume, and presence of significant leakage during filling cystometry.
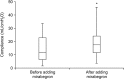
Results: A total of 31 participants with a mean age of 41±15 years were included in the analysis. A significant increase in cystometric capacity (mean, 362 to 424 mL; p=0.03), reflex volume (mean, 251 to 329 mL; p=0.02), and bladder compliance (median, 12 to 18 mL/cmH2O; p=0.04) was observed. The presence of leakage during filling cystometry was significantly reduced (29% to 10%; p=0.03). Likewise, a non-significant decrease in the change in maximal detrusor pressure was observed (mean, 31 to 27 cmH2O; p=0.39).
Conclusion: Adding mirabegron to conventional antimuscarinics further improved urodynamic parameters in patients with chronic SCI, and sustained efficacy was observed in long-term use.
Keywords: Mirabegron; Muscarinic antagonists; Spinal cord injuries; Urodynamics.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
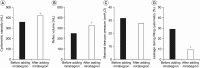
Similar articles
-
Normal ranges of variability for urodynamic studies of neurogenic bladders in spinal cord injury.J Spinal Cord Med. 2006;29(1):26-31. doi: 10.1080/10790268.2006.11753853. J Spinal Cord Med. 2006. PMID: 16572562 Free PMC article.
-
Renal deterioration after spinal cord injury is associated with length of detrusor contractions during cystometry-A study with a median of 41 years follow-up.Neurourol Urodyn. 2017 Aug;36(6):1607-1615. doi: 10.1002/nau.23163. Epub 2016 Nov 4. Neurourol Urodyn. 2017. PMID: 27813141
-
Urodynamic Efficacy and Safety of Mirabegron Add-on Treatment with Tamsulosin for Japanese Male Patients with Overactive Bladder.Low Urin Tract Symptoms. 2016 Sep;8(3):171-6. doi: 10.1111/luts.12091. Epub 2015 Feb 17. Low Urin Tract Symptoms. 2016. PMID: 27619782
-
Initial experience with the treatment of neurogenic detrusor overactivity with a new β-3 agonist (mirabegron) in patients with spinal cord injury.Spinal Cord. 2016 Jan;54(1):78-82. doi: 10.1038/sc.2015.195. Epub 2015 Oct 27. Spinal Cord. 2016. PMID: 26503222
-
Long-term safety and efficacy of antimuscarinic add-on therapy in patients with overactive bladder who had a suboptimal response to mirabegron monotherapy: A multicenter, randomized study in Japan (MILAI II study).Int J Urol. 2019 Mar;26(3):342-352. doi: 10.1111/iju.13868. Epub 2018 Dec 13. Int J Urol. 2019. PMID: 30548692 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Drug Repurposing for Spinal Cord Injury: Progress Towards Therapeutic Intervention for Primary Factors and Secondary Complications.Pharmaceut Med. 2023 Nov;37(6):463-490. doi: 10.1007/s40290-023-00499-3. Epub 2023 Sep 12. Pharmaceut Med. 2023. PMID: 37698762 Review.
-
Lower urinary tract dysfunction in common neurological diseases.Turk J Urol. 2020 Nov;46(Supp. 1):S70-S78. doi: 10.5152/tud.2020.20092. Epub 2020 Apr 30. Turk J Urol. 2020. PMID: 32384046 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gerridzen RG, Thijssen AM, Dehoux E. Risk factors for upper tract deterioration in chronic spinal cord injury patients. J Urol. 1992;147:416–8. - PubMed
-
- Goldmark E, Niver B, Ginsberg DA. Neurogenic bladder: from diagnosis to management. Curr Urol Rep. 2014;15:448. - PubMed
-
- Abrams P, Artibani W, Gajewski JB, Hussain I. Assessment of treatment outcomes in patients with overactive bladder: importance of objective and subjective measures. Urology. 2006;68(2 Suppl):17–28. - PubMed
-
- del Popolo G, Mencarini M, Nelli F, Lazzeri M. Controversy over the pharmacological treatments of storage symptoms in spinal cord injury patients: a literature overview. Spinal Cord. 2012;50:8–13. - PubMed
-
- Benner JS, Nichol MB, Rovner ES, Jumadilova Z, Alvir J, Hussein M, et al. Patient-reported reasons for discontinuing overactive bladder medication. BJU Int. 2010;105:1276–82. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

