Discovery and Structural Optimization of Acridones as Broad-Spectrum Antimalarials
- PMID: 30852885
- PMCID: PMC6822569
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b01961
Discovery and Structural Optimization of Acridones as Broad-Spectrum Antimalarials
Abstract
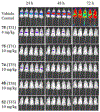
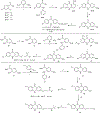
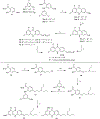
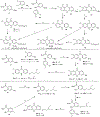
Malaria remains one of the deadliest diseases in the world today. Novel chemoprophylactic and chemotherapeutic antimalarials are needed to support the renewed eradication agenda. We have discovered a novel antimalarial acridone chemotype with dual-stage activity against both liver-stage and blood-stage malaria. Several lead compounds generated from structural optimization of a large library of novel acridones exhibit efficacy in the following systems: (1) picomolar inhibition of in vitro Plasmodium falciparum blood-stage growth against multidrug-resistant parasites; (2) curative efficacy after oral administration in an erythrocytic Plasmodium yoelii murine malaria model; (3) prevention of in vitro Plasmodium berghei sporozoite-induced development in human hepatocytes; and (4) protection of in vivo P. berghei sporozoite-induced infection in mice. This study offers the first account of liver-stage antimalarial activity in an acridone chemotype. Details of the design, chemistry, structure-activity relationships, safety, metabolic/pharmacokinetic studies, and mechanistic investigation are presented herein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
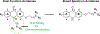
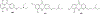

References
-
- WHO. World malaria report. 2016.
-
- White NJ; Pukrittayakamee S; Hien TT; Faiz MA; Mokuolu OA; Dondorp AM. Malaria. Lancet 2014, 383, 723–735. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

