Histopathologic and Genetic Features of Alveolar Capillary Dysplasia with Atypical Late Presentation and Prolonged Survival
- PMID: 30853201
- PMCID: PMC6592752
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2019.01.047
Histopathologic and Genetic Features of Alveolar Capillary Dysplasia with Atypical Late Presentation and Prolonged Survival
Abstract
Alveolar capillary dysplasia typically presents with neonatal pulmonary hypertension and early mortality. However, there is growing evidence for a subset of disease with atypical late onset and/or prolonged survival. Here, we present the variable clinical, genetic, and pathology findings of 4 such patients.
Keywords: ACD; FOXF1; MPV; case report.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
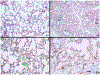
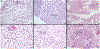
References
-
- Mac MH. Congenital alveolar dysplasia of the lungs. Bull New Engl Med Cent. 1947; 9: 48. - PubMed
-
- Eulmesekian P, Cutz E, Parvez B, Bohn D, Adatia I. Alveolar capillary dysplasia: a six-year single center experience. J Perinat Med. 2005; 33: 347–52. - PubMed
-
- Michalsky MP, Arca MJ, Groenman F, Hammond S, Tibboel D, Caniano DA. Alveolar capillary dysplasia: a logical approach to a fatal disease. J Pediatr Surg. 2005; 40: 1100–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

