Association between p53 Expression and Amount of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- PMID: 30853706
- PMCID: PMC6527934
- DOI: 10.4132/jptm.2019.02.08
Association between p53 Expression and Amount of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Abstract
Background: Most triple-negative breast cancers (TNBCs) have a high histologic grade, are associated with high endoplasmic stress, and possess a high frequency of TP53 mutations. TP53 missense mutations lead to the production of mutant p53 protein and usually show high levels of p53 protein expression. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) accumulate as part of the anti-tumor immune response and have a strong prognostic and predictive significance in TNBC. We aimed to elucidate the association between p53 expression and the amount of TILs in TNBC.
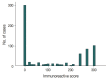
Methods: In 678 TNBC patients, we evaluated TIL levels and expression of endoplasmic stress molecules. Immunohistochemical examination of p53 protein expression was categorized into three groups: no, low, and high expression.
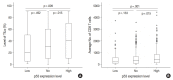
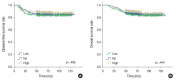
Results: No, low, and high p53 expression was identified in 44.1% (n = 299), 20.1% (n = 136), and 35.8% (n = 243) of patients, respectively. Patients with high p53 expression showed high histologic grade (p < .001), high TIL levels (p = .009), and high expression of endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated molecules (p-eIF2a, p = .013; XBP1, p = .007), compared to patients with low p53 expression. There was no significant difference in disease-free (p = .406) or overall survival rates (p = .444) among the three p53 expression groups.
Conclusions: High p53 expression is associated with increased expression of endoplasmic reticulum stress molecules and TIL influx.
Keywords: Breast neoplasms; Lymphocytes, Tumor-infiltrating; p53.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Yamashita N, Kondo M, Zhao S, et al. Picrasidine G decreases viability of MDA-MB 468 EGFR-overexpressing triple-negative breast cancer cells through inhibition of EGFR/STAT3 signaling pathway. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2017;27:2608–12. - PubMed
-
- van Rooijen JM, Stutvoet TS, Schroder CP, de Vries EG. Immunotherapeutic options on the horizon in breast cancer treatment. Pharmacol Ther. 2015;156:90–101. - PubMed
-
- Kim JY, Heo SH, Song IH, et al. Activation of the PERK-eIF2alpha pathway is associated with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in HER2-positive breast cancer. Anticancer Res. 2016;36:2705–11. - PubMed
-
- Kim YA, Lee HJ, Heo SH, et al. MxA expression is associated with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and is a prognostic factor in triplenegative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2016;156:597–606. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

